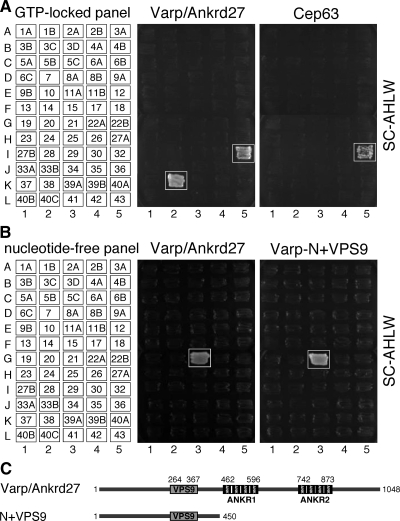
Figure 1.
Rab binding specificity of Varp as revealed by yeast two-hybrid panels. (A) Specific interaction of Varp-Full with the GTP-fixed form of Rab32 and Rab38, and of Cep63 with the GTP-fixed form of Rab32. Yeast cells containing pGBD plasmid expressing GTP-locked Rab protein (positions indicated in the left panels) and pAct2 plasmid expressing Varp (or Cep63) protein were streaked on SC-AHLW and incubated at 30°C. Positive patches are boxed. (B) Specific interaction of Varp-Full and Varp-N+VPS9 with the nucleotide-free form of Rab21. Yeast cells containing pGBD plasmid expressing Varp protein and pGAD plasmid expressing nucleotide-free Rab (positions indicated in the left panels) were streaked on SC-AHLW and incubated at 30°C. Positive patches are boxed. (C) Schematic representation of Varp and its truncated mutant Varp-N+VPS9 used in A and B. Varp contains an N-terminal VPS9 domain and C-terminal tandem ankyrin repeats (named ANKR1 and ANKR2).