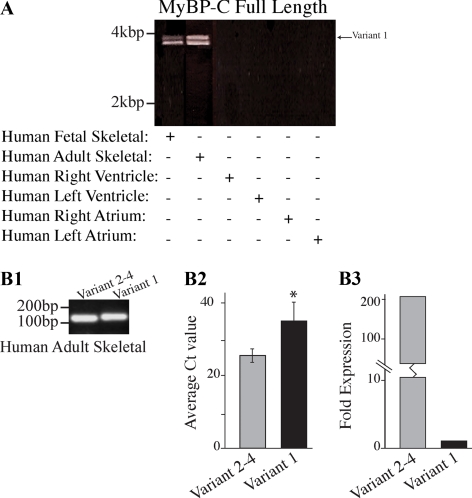
Figure 4.
Molecular characterization of MyBP-C slow variant-1 in human skeletal muscle during development and at maturity. (A) RT-PCR was used to amplify full-length MyBP-C slow transcripts. Adult and fetal skeletal muscle cDNA of human origin was amplified using primers, forward-8 and reverse-8 that flanked the 5′ and 3′ UTR regions, respectively. Two major bands of ∼4 and ∼3.8 kbp were obtained in both samples. Notably, no amplification product was detected when cDNA from right or left ventricles and atria was used. Sequence analysis of the fetal and adult products indicated that the top band corresponds to MyBP-C slow variant-1 (NM_002456), whereas the lower band corresponds to a mixed population of variants 2–4 (NM_206819, NM_206820, and NM_206821). (B1) RT-PCR using human skeletal muscle RNA and primer sets designed to specifically amplify the unique COOH terminus of variant-1 (primers F9/R9) or the common COOH terminus of variants 2–4 (primers F9/R10). (B2) Quantification of the mRNA levels of MyBP-C slow variant-1 and variants 2–4 expressed as average Ct values (n = 5; p < 0.01). (B3) Average Ct values from five independent experiments were used to calculate the -fold difference of the expression levels of variant-1 compared with variants 2–4; these indicated that variant-1 is expressed in lower amounts (∼200-fold difference) compared with variants 2–4.