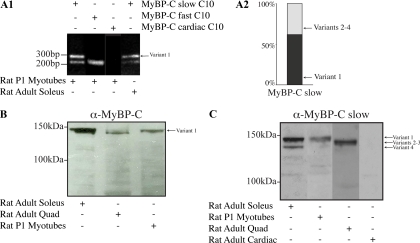
Figure 5.
Molecular characterization of MyBP-C slow variant-1 in rat skeletal muscle during development and at maturity. (A1) RT-PCR was performed using rat cDNA from adult soleus muscle or cultures of P1 skeletal myotubes and primers forward-5 and reverse-8 located in the C10 domain and the 3′ UTR, respectively. Two PCR products were generated with sizes of ∼325 and ∼250 nt. Sequence analysis indicated that the longer product (∼325 nt) included the C10 domain together with the unique COOH-terminal 79 nucleotides, corresponding to variant-1, whereas the smaller product (∼250 nt) contained the C10 domain followed by the 12-nucleotide-long COOH terminus found in variants 2–4. cDNA prepared from primary cultures of skeletal myotubes also contained transcripts of the fast isoform (∼220 nt) but not of the cardiac isoform (for both the fast and cardiac isoforms the primers sets were designed to anneal to sequences present in the respective C10 repeats and their 3′ UTRs). (A2) Semiquantitative analysis, using five independent experiments, of the relative expression levels of MyBP-C slow variants in cultures of rat skeletal myotubes demonstrated that variant-1 composes ∼60% of the total MyBP-C slow population. (B) Protein homogenates of rat origin were prepared from adult soleus and quadriceps skeletal muscles and P1 skeletal myotubes cultured for 7 d. These were immunoprobed with a MyBP-C antibody that recognizes all forms of MyBP-C (slow, fast, and cardiac; pan MyBP-C; B) or an antibody specific for the slow isoforms (C). Two closely migrating bands of ∼126–129 and ∼132 kDa were detected in homogenates prepared from slow twitch soleus muscle whereas a main band of ∼126–129 kDa was detected in homogenates prepared from fast twitch quadriceps muscle. Notably, homogenates prepared from P1 myotubes contained a main band of ∼132 kDa. (C) Use of a different gel system (see Materials and Methods) that allowed better separation of the closely migrating bands detected with the pan-MyBP-C antibody, and of an antibody that specifically recognizes the slow forms of MyBP-C also demonstrated the presence of a main band of ∼132 kDa in soleus and P1 myotube homogenates and a less prominent band of ∼126 kDa in soleus, which correspond to variant-1 and variant-4, respectively. To the contrary, a prominent immunoreactive band of ∼128–129 kDa was detected in quadriceps homogenates, which was absent from soleus and P1 lysates, and may represent a mixed population of variants 2 and 3. No immunoreactive band was detected in lysates prepared from heart muscle, which confirmed the specificity of the antibody used.