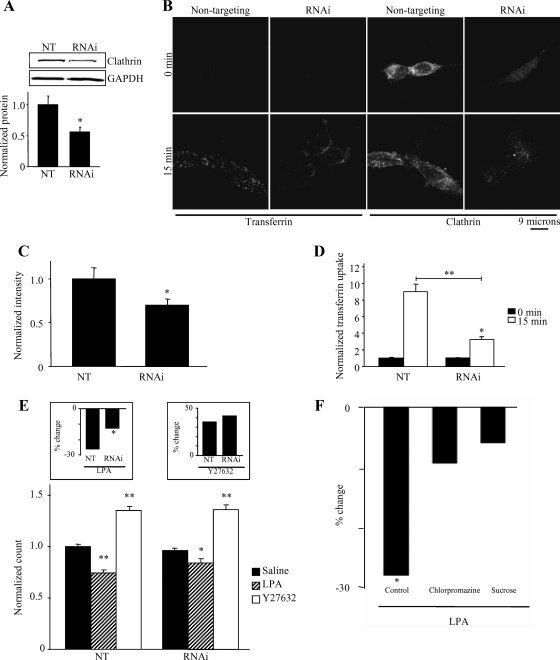
Figure 4.
LPA-induced endocytosis of Kv1.2 is clathrin dependent. (A) Transfection of HEK-K cells with siRNA directed against the heavy chain of human clathrin depletes clathrin protein by 50% compared with nontargeting siRNA control. Clathrin heavy chain protein was detected with α-CHCm. GAPDH was detected with α-GAPDHm as a loading control. Bar graph represents quantification of eight individual experiments (n = 8; *p = 0.008). (B) Immunofluorescence of single optical slices through the center of HEK-K cells illustrates that clathrin siRNA reduces clathrin signal intensity and reduced the number of internalized Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated transferrin-containing puncta compared with nontargeting control both at 0- and 15-min incubation at 37°C. Clathrin heavy chain was detected with α-CHCm. (C) Quantitation of immunofluorescence images reveals that clathrin siRNA reduces clathrin signal intensity by ∼30% compared with nontargeting control (n = 37; *p = 0.035). (D) Quantitation of immunofluorescence images reveals that transferrin uptake is reduced threefold in cells with clathrin siRNA compared with cells with nontargeting siRNA control (n = 17; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001). (E) Flow cytometric analysis of HEK-K cells reveals that clathrin siRNA reduces LPA-induced endocytosis of Kv1.2, while having no effect on steady-state surface Kv1.2 levels. Treatment with Y27632 (10 μM; 30 min) significantly increases surface Kv1.2 both in the absence or presence of clathrin siRNA (n = 33; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001). Inset, left, LPA-induced Kv1.2 endocytosis is significantly reduced in the presence of clathrin siRNA (n = 33; *p < 0.05). Inset, right, effect of Y27632 is not significantly altered in the absence or presence of clathrin siRNA (n = 33; p = 0.493). (F) Inhibiting clathrin dependent endocytosis with chlorpromazine or hypertonic sucrose inhibits LPA-induced KV1.2 endocytosis. The percentage of reduction in surface Kv1.2 elicited by LPA in control cells was significant (n = 26; *p < 0.01); however, LPA had no significant effect in cells pretreated with chlorpromazine (n = 18; p = 0.21) or by hypertonic sucrose (n = 9; p = 0.19).