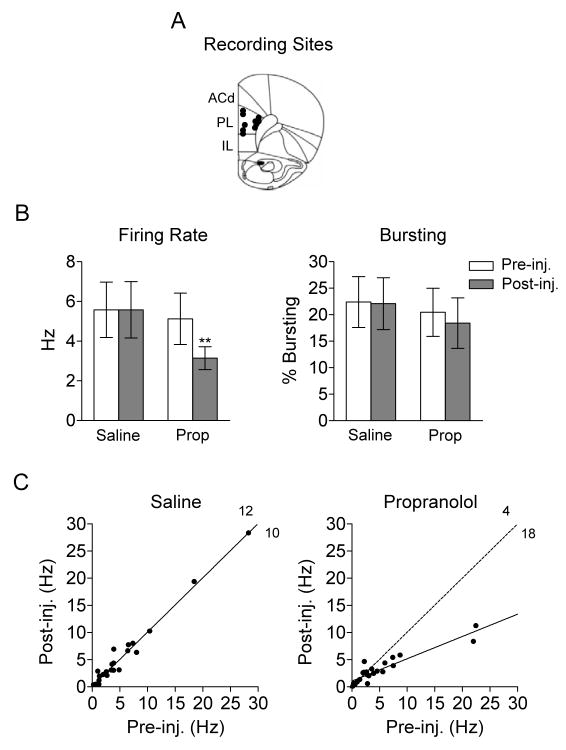
Figure 5.
Propranolol reduces spontaneous firing rate of prelimbic (PL) neurons in awake rats. (A) Unit recording sites in PL (IL: infralimbic cortex; ACd: dorsal anterior cingulate cortex). (B) Systemic propranolol decreased spontaneous firing rate (**p<0.01), but not bursting, in PL neurons. (C) The firing rates of individual neurons before and after injection are shown. Unlike saline, injection of propranolol decreased the firing rate of the majority of neurons (p<0.05). Solid lines in each plot represent the linear regression; dotted line in the propranolol plot represents the linear regression of the saline results. (propranolol: Prop; injection: inj.)