Abstract
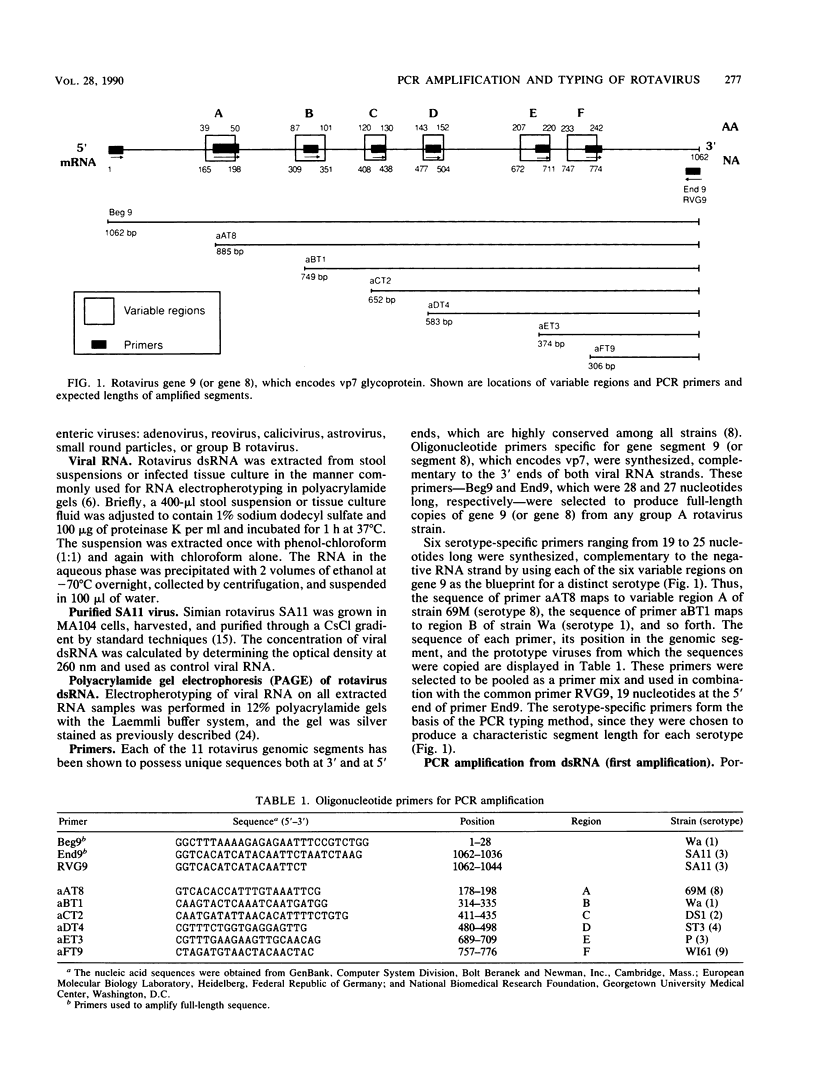
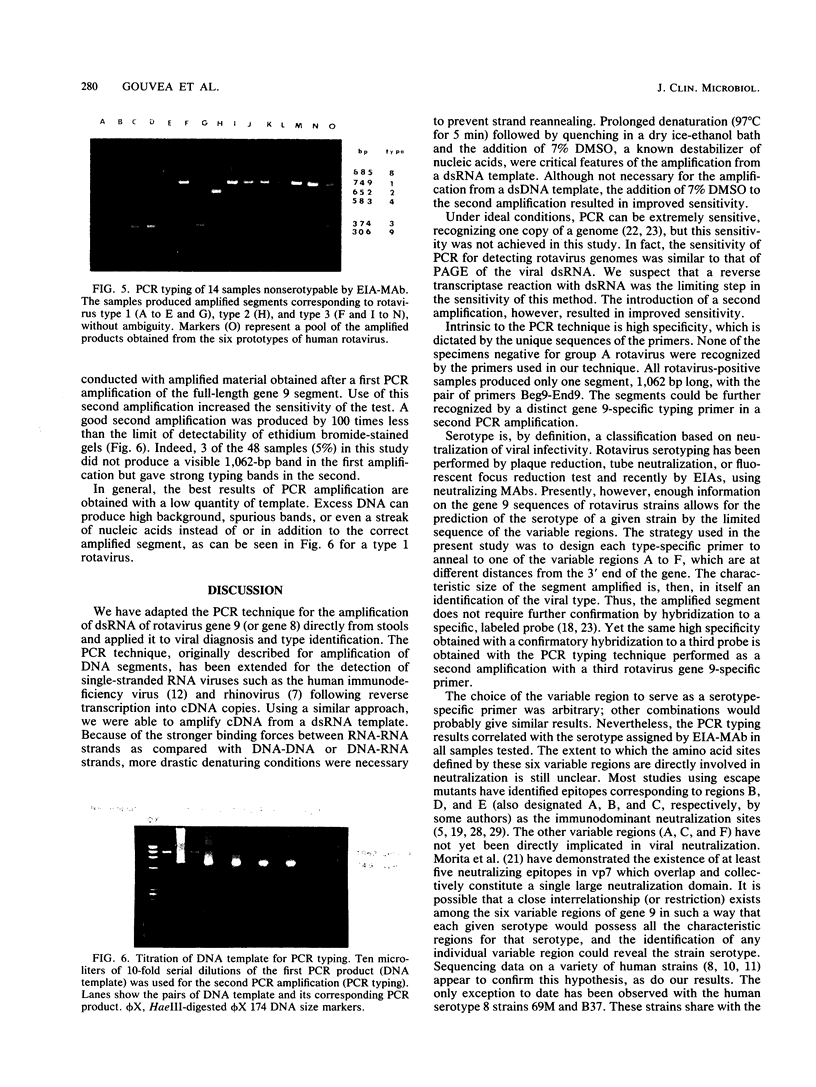
The rotavirus gene segment coding for the major outer capsid glycoprotein vp7 was amplified directly from stool specimens by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Double-stranded RNA extracted from stool samples was used as the template for reverse transcription, which was followed immediately and in the same reaction mix with amplification, using the Taq polymerase. Various conditions were examined to optimize the yield of the amplified gene. The concentrations of MgCl2, dimethyl sulfoxide, and template RNA were critical. The choice of primer pairs allowed amplification of the entire segment or specific portions. By using type-specific primers derived from distinct regions on the gene, we devised a PCR typing method in which each human serotype virus produced a characteristic segment size, readily identifiable in agarose gels. The PCR typing method was applied to 10 rotavirus reference strains, including all 6 known human serotypes (serotypes 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, and 9), and to 34 stool specimens previously serotyped by an enzyme immunoassay with monoclonal antibodies. An absolute correlation was found between the molecular and serologic methods. In addition, 14 stool specimens nonserotypable by an enzyme immunoassay with monoclonal antibodies could be typed by the PCR method. Besides the application for rotavirus detection and typing directly from stools, the PCR method provides a rapid and efficient means of obtaining large quantities of cDNA suitable for sequencing, cloning, and other genetic studies, precluding the need for cell culture and virus purification.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bastardo J. W., McKimm-Breschkin J. L., Sonza S., Mercer L. D., Holmes I. H. Preparation and characterization of antisera to electrophoretically purified SA11 virus polypeptides. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):641–647. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.641-647.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beards G. M., Pilfold J. N., Thouless M. E., Flewett T. H. Rotavirus serotypes by serum neutralisation. J Med Virol. 1980;5(3):231–237. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890050307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark H. F., Hoshino Y., Bell L. M., Groff J., Hess G., Bachman P., Offit P. A. Rotavirus isolate WI61 representing a presumptive new human serotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1757–1762. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1757-1762.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson B. S., Tursi J. M., McAdam W. J., Bishop R. F. Derivation of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to human rotaviruses and evidence that an immunodominant neutralization site is shared between serotypes 1 and 3. Virology. 1986 Oct 30;154(2):302–312. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90456-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyall-Smith M. L., Lazdins I., Tregear G. W., Holmes I. H. Location of the major antigenic sites involved in rotavirus serotype-specific neutralization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3465–3468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Palmer E. L., Obijeski J. F. Rotaviruses: a review. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;105:123–184. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69159-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gama R. E., Hughes P. J., Bruce C. B., Stanway G. Polymerase chain reaction amplification of rhinovirus nucleic acids from clinical material. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9346–9346. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass R. I., Keith J., Nakagomi O., Nakagomi T., Askaa J., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M., Flores J. Nucleotide sequence of the structural glycoprotein VP7 gene of Nebraska calf diarrhea virus rotavirus: comparison with homologous genes from four strains of human and animal rotaviruses. Virology. 1985 Mar;141(2):292–298. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90260-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. Y., Hoshino Y., Ikegami N. Sequence analysis of the gene encoding the serotype-specific glycoprotein (VP7) of two new human rotavirus serotypes. Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):429–433. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90289-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. Y., Midthun K., Gorziglia M., Hoshino Y., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M., Flores J. Comparison of the amino acid sequences of the major neutralization protein of four human rotavirus serotypes. Virology. 1987 Nov;161(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. Y., Sears J. F., Taniguchi K., Midthun K., Hoshino Y., Gorziglia M., Nishikawa K., Urasawa S., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Prediction of human rotavirus serotype by nucleotide sequence analysis of the VP7 protein gene. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1819–1823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1819-1823.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Valdesuso J., van Wyke K., Midthun K., Walsh M., McAuliffe V., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Hoshino Y. Production and preliminary characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed at two surface proteins of rhesus rotavirus. J Virol. 1983 Aug;47(2):267–275. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.2.267-275.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart C., Schochetman G., Spira T., Lifson A., Moore J., Galphin J., Sninsky J., Ou C. Y. Direct detection of HIV RNA expression in seropositive subjects. Lancet. 1988 Sep 10;2(8611):596–599. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90639-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath R., Birch C., Gust I. Antigenic analysis of rotavirus isolates using monoclonal antibodies specific for human serotypes 1, 2, 3 and 4, and SA11. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2455–2466. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Serotypic similarity and diversity of rotaviruses of mammalian and avian origin as studied by plaque-reduction neutralization. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):694–702. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hum C. P., Dyall-Smith M. L., Holmes I. H. The VP7 gene of a new G serotype of human rotavirus (B37) is similar to G3 proteins in the antigenic c region. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):55–61. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90351-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki E. S., Clark S. S., Coyne M. Y., Smith S. D., Champlin R., Witte O. N., McCormick F. P. Diagnosis of chronic myeloid and acute lymphocytic leukemias by detection of leukemia-specific mRNA sequences amplified in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5698–5702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackow E. R., Shaw R. D., Matsui S. M., Vo P. T., Benfield D. A., Greenberg H. B. Characterization of homotypic and heterotypic VP7 neutralization sites of rhesus rotavirus. Virology. 1988 Aug;165(2):511–517. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90595-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Hasegawa A., Mukoyama A., Inouye S. A candidate for a new serotype of human rotavirus. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):623–624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.623-624.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita Y., Taniguchi K., Urasawa T., Urasawa S. Analysis of serotype-specific neutralization epitopes on VP7 of human rotavirus by the use of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies and antigenic variants. J Gen Virol. 1988 Feb;69(Pt 2):451–458. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-2-451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oste C. Polymerase chain reaction. Biotechniques. 1988 Feb;6(2):162–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira H. G., Gouvea V. S., Fialho A. M. A comparison of simian rotavirus SA11 preparations maintained in different laboratories. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1986 Oct-Dec;81(4):389–393. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02761986000400005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. D., Stoner-Ma D. L., Estes M. K., Greenberg H. B. Specific enzyme-linked immunoassay for rotavirus serotypes 1 and 3. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):286–291. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.286-291.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. D., Vo P. T., Offit P. A., Coulson B. S., Greenberg H. B. Antigenic mapping of the surface proteins of rhesus rotavirus. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):434–451. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonza S., Breschkin A. M., Holmes I. H. Derivation of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies against rotavirus. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1143–1146. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1143-1146.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonza S., Breschkin A. M., Holmes I. H. The major surface glycoprotein of simian rotavirus (SA11) contains distinct epitopes. Virology. 1984 Apr 30;134(2):318–327. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90300-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Hoshino Y., Nishikawa K., Green K. Y., Maloy W. L., Morita Y., Urasawa S., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M., Gorziglia M. Cross-reactive and serotype-specific neutralization epitopes on VP7 of human rotavirus: nucleotide sequence analysis of antigenic mutants selected with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1870–1874. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1870-1874.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Urasawa S., Urasawa T. Preparation and characterization of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies with different reactivity patterns to human rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1985 May;66(Pt 5):1045–1053. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-5-1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Urasawa T., Morita Y., Greenberg H. B., Urasawa S. Direct serotyping of human rotavirus in stools by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using serotype 1-, 2-, 3-, and 4-specific monoclonal antibodies to VP7. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1159–1166. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urasawa S., Urasawa T., Taniguchi K., Wakasugi F., Kobayashi N., Chiba S., Sakurada N., Morita M., Morita O., Tokieda M. Survey of human rotavirus serotypes in different locales in Japan by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with monoclonal antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jul;160(1):44–51. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.1.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., James W. D., Pittman A. L., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Definition of human rotavirus serotypes by plaque reduction assay. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):110–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.110-115.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]