Abstract
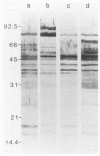
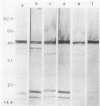
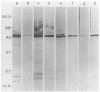
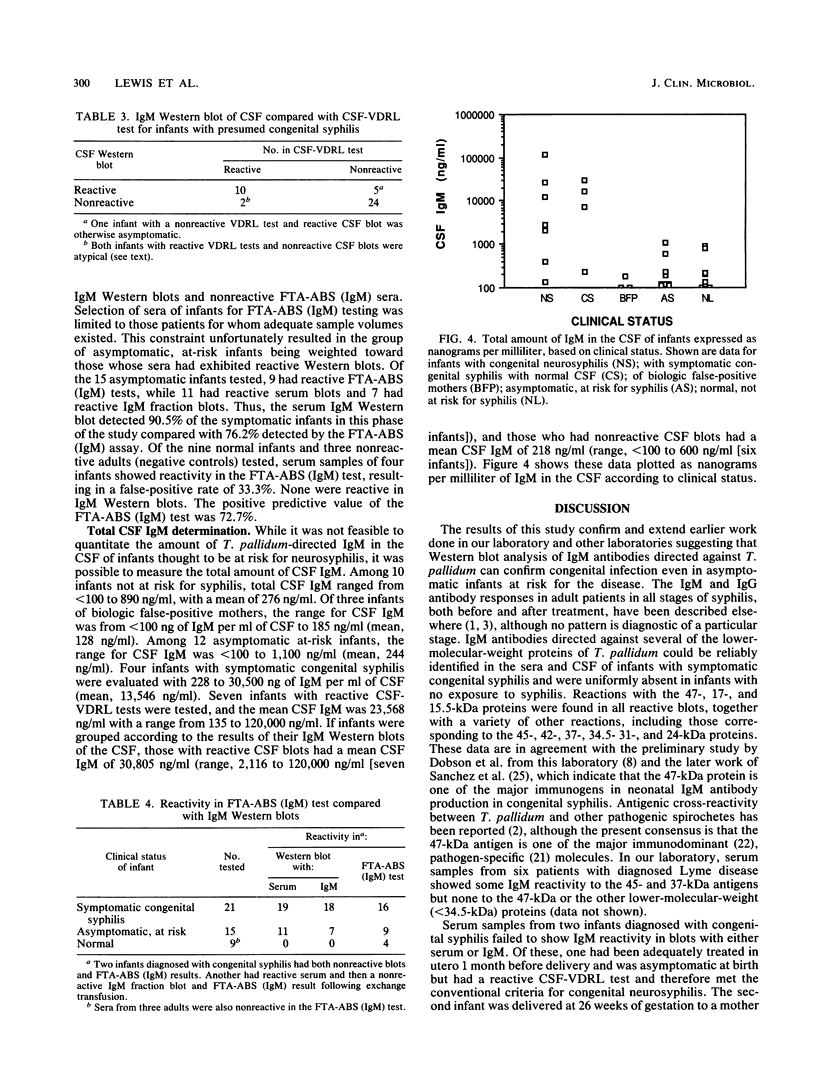
Western immunoblots of solubilized Treponema pallidum antigens were reacted with sera and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and developed with enzyme-conjugated antibodies to immunoglobulin M (IgM). A blot was considered positive if reactions included bands at the 47-, 17-, and 15.5-kilodalton positions along with a variable pattern at other low-molecular-weight positions. Sera from 23 of 25 symptomatic infants diagnosed with congenital syphilis yielded positive reactions. Of 80 asymptomatic infants considered at risk for developing symptomatic infection, 16 exhibited IgM patterns consistent with those seen in congenital syphilis, although 5 of these 16 gave reactions that were equivocal. To exclude false-positive reactions due to IgM rheumatoid factor, sera were fractionated and the IgM fractions were retested. Only the five initially equivocal sera gave nonreactive blots with the IgM fractions, whereas all others gave more prominent reactions that were qualitatively similar to those seen in serum samples. Sera from 18 normal infants failed to show any IgM reactivity to T. pallidum antigens on Western blots. The IgM Western blot was both more sensitive and more specific than the fluorescent treponemal antibody-absorbed (IgM) test using fractionated serum. Of the 17 CSF samples from infants with symptomatic congenital syphilis, 14 showed IgM reactivity in Western blots, whereas only 12 had a reactive CSF in the Venereal Disease Research Laboratory test. Our results indicate that this technique can be used to identify both symptomatic and asymptomatic infection in infants with T. pallidum, in some cases before standard serologic studies can confirm the diagnosis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker-Zander S. A., Hook E. W., 3rd, Bonin P., Handsfield H. H., Lukehart S. A. Antigens of Treponema pallidum recognized by IgG and IgM antibodies during syphilis in humans. J Infect Dis. 1985 Feb;151(2):264–272. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.2.264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker-Zander S. A., Lukehart S. A. Antigenic cross-reactivity between Treponema pallidum and other pathogenic members of the family Spirochaetaceae. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):116–121. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.116-121.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker-Zander S. A., Roddy R. E., Handsfield H. H., Lukehart S. A. IgG and IgM antibody reactivity to antigens of Treponema pallidum after treatment of syphilis. Sex Transm Dis. 1986 Oct-Dec;13(4):214–220. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198610000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baughn R. E., Musher D. M. Isolation and preliminary characterization of circulating immune complexes from rabbits with experimental syphilis. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):579–584. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.579-584.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson S. R., Taber L. H., Baughn R. E. Recognition of Treponema pallidum antigens by IgM and IgG antibodies in congenitally infected newborns and their mothers. J Infect Dis. 1988 May;157(5):903–910. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.5.903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farshy C. E., Hunter E. F., Larsen S. A., Cerny E. H. Double-conjugate enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for immunoglobulins G and M against Treponema pallidum. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1109–1113. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1109-1113.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryden A., Link H., Norrby E. Cerebrospinal fluid and serum immunoglobulins and antibody titers in mumps meningitis and aseptic meningitis of other etiology. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):852–861. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.852-861.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. B., Jr, Libby R. Separation of immunoglobulin M (IgM) essentially free of IgG from serum for use in systems requiring assay of IgM-type antibodies without interference from rheumatoid factor. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):451–454. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.451-454.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judge D. M., Tafari N., Naeye R. L., Marboe C. Congenital syphilis and perinatal mortality. Pediatr Pathol. 1986;5(3-4):411–420. doi: 10.3109/15513818609068867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. E., Olansky D. C., Wiesner P. J. The FTA-ABS (IgM) test for neonatal congenital syphilis: A critical review. J Am Vener Dis Assoc. 1974 Dec;1(2):79–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane G. K., Oates R. K. Congenital syphilis has not disappeared. Med J Aust. 1988 Feb 15;148(4):171–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKown R. R., Kapernick P. S. Syphilis in pregnancy. South Med J. 1988 Apr;81(4):447–451. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198804000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller F., Moskophidis M., Borkhardt H. L. Detection of immunoglobulin M antibodies to Treponema pallidum in a modified enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;6(1):35–39. doi: 10.1007/BF02097187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller F. Specific immunoglobulin M and G antibodies in the rapid diagnosis of human treponemal infections. Diagn Immunol. 1986;4(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V., Chamberlain N. R., Swancutt M. A., Goldberg M. S. Cloning and expression of the major 47-kilodalton surface immunogen of Treponema pallidum in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):500–506. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.500-506.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. S., Orum O., Mouritsen S. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibodies to the venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL) antigen in syphilis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1711–1716. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1711-1716.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer C. B., Black C. M., Phillips D. J., Logan L. C., Hunter E. F., Pender B. J., McGrew B. E. The specificity of fetal IgM: antibody or anti-antibody? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;254:77–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29159.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz K. F., Cates W., Jr, O'Mara P. R. Pregnancy loss, infant death, and suffering: legacy of syphilis and gonorrhoea in Africa. Genitourin Med. 1987 Oct;63(5):320–325. doi: 10.1136/sti.63.5.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotti A. T., Logan L. A specific IgM antibody test in neonatal congenital syphilis. J Pediatr. 1968 Aug;73(2):242–243. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sindic C. J., Cambiaso C. L., Depré A., Laterre E. C., Masson P. L. The concentration of IgM in the cerebrospinal fluid of neurological patients. J Neurol Sci. 1982 Sep;55(3):339–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90131-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smikle M. F., James O. B., Prabhakar P. Diagnosis of neurosyphilis: a critical assessment of current methods. South Med J. 1988 Apr;81(4):452–454. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198804000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens M. C., Darbyshire P. J., Brown S. M. Early congenital syphilis and severe haematological disturbance. Arch Dis Child. 1987 Oct;62(10):1073–1075. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.10.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez P. J., McCracken G. H., Jr, Wendel G. D., Olsen K., Threlkeld N., Norgard M. V. Molecular analysis of the fetal IgM response to Treponema pallidum antigens: implications for improved serodiagnosis of congenital syphilis. J Infect Dis. 1989 Mar;159(3):508–517. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.3.508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley J. D., Kaplan J. M., Holmes R. K., McCracken G. H., Jr, Sanford J. P. Passive transfer of antibodies of maternal origin from blood to cerebrospinal fluid in infants. Lancet. 1975 Mar 22;1(7908):651–653. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91757-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolters E. C. Neurosyphilis: a changing diagnostic problem? Eur Neurol. 1987;26(1):23–28. doi: 10.1159/000116306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eijk R. V., Wolters E. C., Tutuarima J. A., Hische E. A., Bos J. D., van Trotsenburg L., de Koning G. A., van der Helm H. J. Effect of early and late syphilis on central nervous system: cerebrospinal fluid changes and neurological deficit. Genitourin Med. 1987 Apr;63(2):77–82. doi: 10.1136/sti.63.2.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]