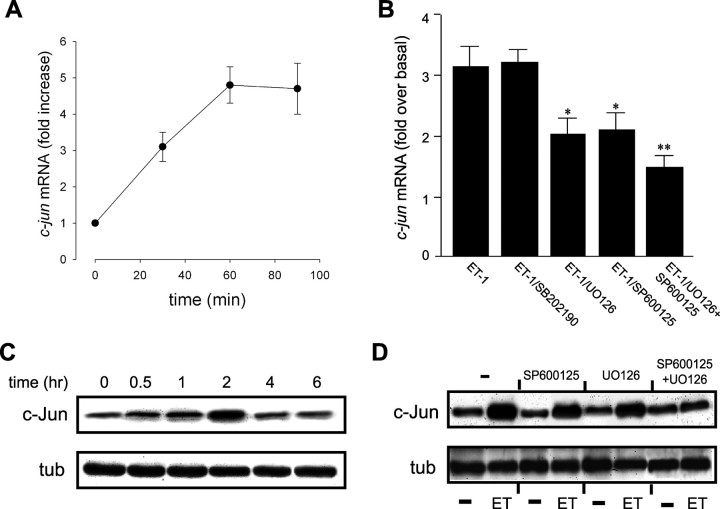
Figure 8.
ET-1 increases c-jun expression via multiple signaling transduction pathways. A, Time course of ET-1-induced c-jun mRNA expression. Cells were stimulated with 100 nm ET-1 for the indicated times, and total RNA was extracted and processed for quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis. Data are averages ± SEM (n = 3–4 independent experiments). B, ET-1 increases c-jun mRNA expression through activation of ERK/JNK-dependent pathways. Cells were preincubated for 30 min with one of the following inhibitors: p38MAPK inhibitor SB202190 (10 mm), the MEK inhibitor U0126 (10 mm), the JNK inhibitor SP600125 (10 mm), or a combination of U0126 and SP600125. For c-jun mRNA quantification, cells were treated for 60 min with ET-1, and total RNA was processed as described above. Data are averages ± SEM (n = 3–4 independent experiments). *p < 0.001 versus ET-1. **p < 0.05 versus U0126 and SP600125 alone; **p < 0.001 versus ET-1 (Student's t test). C, Time course of ET-1-induced c-jun protein expression. Cells were stimulated with 100 nm ET-1 for the indicated times, and total cell lysates were analyzed by Western blot using an anti-c-jun antibody (C, top) or an anti-tubulin antibody (C, bottom) for normalization of total amount of loaded proteins. D, ET-1 increases c-jun protein expression through activation of ERK/JNK-dependent pathways. Cells were treated with 100 nm ET-1 for 2 h in the presence or absence of inhibitors (see B), and total cell lysates were analyzed by Western blot using an anti-c-jun antibody (D, top) or an anti-tubulin antibody (D, bottom). Note the synergistic effects of SP600125 and U0126 on both ET-1-induced c-jun mRNA and protein expression.