Figure 9.
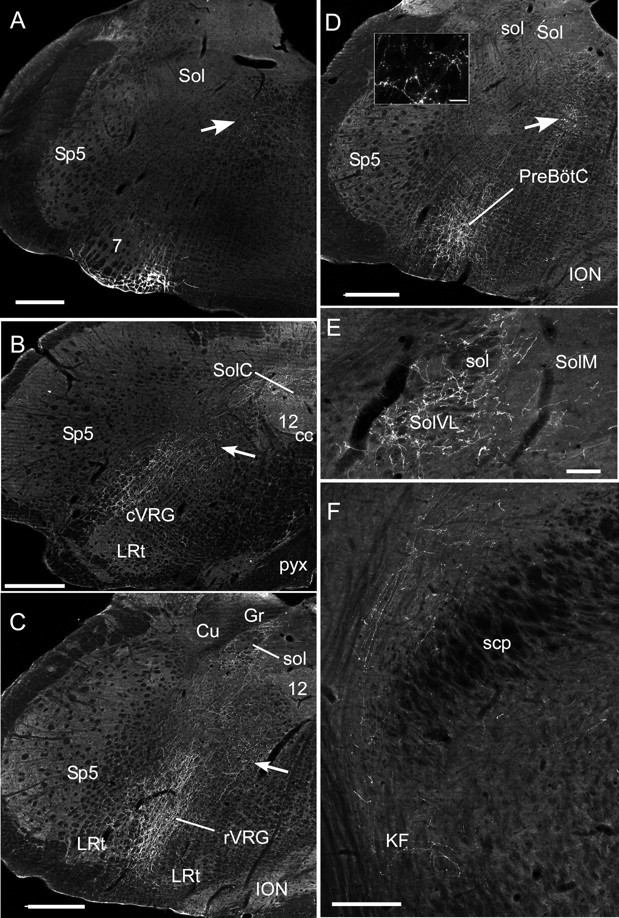
Anatomical projections of the RTN neurons. A, Injection site of PRSX8-ChR2-mCherry lentivirus in the ventrolateral medulla in a rat treated by anti-DBH-saporin to reduce the number of TH neurons that reside in the RTN region. Note that mCherry fluorescence is confined to neurons located just ventral and medial to the facial motor nucleus (7). The arrows in A–D point to transversely cut axons emanating from the labeled neurons. Sp5, Spinal trigeminal nucleus; Sol, nucleus of the solitary tract. Scale bar: A–D, 500 μm. B, Projections to the caudal medulla are confined to the cVRG (caudal ventral respiratory group), the nucleus of the solitary tract, and the region between these areas. 12, Hypoglossal nucleus; cc, central canal; LRt, lateral reticular nucleus; pyx, decussation of the pyramidal tract; SolC, commissural subnucleus of the solitary tract nucleus. Other abbreviations are as in A. C, Projection to the rostral ventral respiratory group (rVRG). Cu, Cuneate nucleus; Gr, gracile nucleus; ION, inferior olivary nucleus; sol, solitary tract. Other abbreviations are as in A and B. The lateral portion of the nucleus of the solitary tract is also heavily innervated. D, Heavy projections to the Pre-Bötzinger complex (PreBötC). The inset illustrates labeled boutons observed in the PreBötC. Scale bar: inset, 25 μm. Abbreviations are as above. E, Projections to the caudal portion of the solitary tract nucleus. Note that most of the boutons are in the interstitial and ventrolateral portions of the nucleus (SolVL) in which respiratory-related neurons reside. Scale bar, 100 μm. SolM, Medial subnucleus of Sol. Other abbreviations are as above. F, Projections to the parabrachial nucleus and Kölliker–Fuse (KF) nucleus. scp, Superior cerebellar peduncle. Scale bar, 250 μm.
