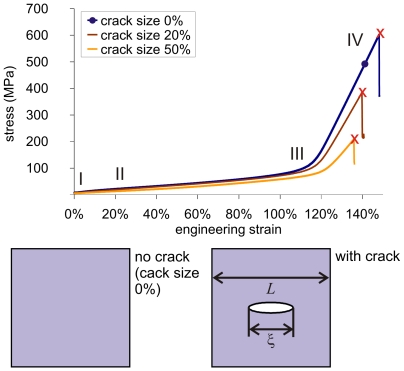
Figure 4. Mechanical response of the alpha-helical protein network.
The graph shows stress-strain curves of a protein network, with and without a crack, as well as for two different crack sizes. The relative crack size is given as ratio of crack length ξ divided by the system size L, defined as χ = ξ / L. We observe two major regimes, (I–III) a very flat increase in stress until approximately 100 MPa, followed (III–IV) by a very steep increase in stress due to strain hardening of the protein backbone up to strains of close to 140..150%. Eventually, strong bonds between different alpha-helical protein chains break, and the entire system fails catastrophically. Interestingly, there exists only little difference in terms of the failure strain between all three systems, indicating the fault tolerance of the studied structure. The perfect system (without a crack) has a strength of ≈600 MPa.