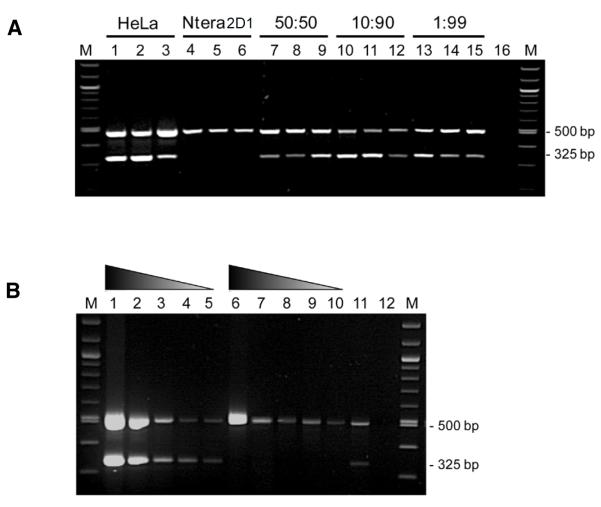
Figure 3. The duplex PCR assay can detect low-level HeLa contamination and can be applied to unpurified cell pellets.
(A) The genotyping assay can detect low-level HeLa DNA contamination. Genomic DNA from the HeLa and Ntera2D1 cell lines was mixed in varying ratios and subjected to PCR amplification in triplicate, using the three-primer duplex genotyping assay. The HeLa-specific AL137164 amplicon is detectable at a ratio of 1% HeLa DNA to 99% NTera2D1 DNA. M, 100-bp ladder molecular weight marker; Lanes 1–3, 100% HeLa genomic DNA (20 ng/reaction); Lanes 4–6, 100% Ntera2D1 DNA (20 ng/reaction); Lanes 7–9, 50% HeLa, 50% Ntera2D1; Lanes 10–12, 10% HeLa, 90% Ntera2D1; Lanes 13–15, 1% HeLa, 99% Ntera2D1; Lane 16, PCR negative control (no input DNA). (B) Unpurified frozen cell pellets are suitable genotyping substrates. Frozen cell pellets (~1 × 106 cells/mL) from HeLa and non-HeLa cell cultures were defrosted, diluted in 5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.0 and boiled for 5 min. The boiled extracts were amplified using the three-primer duplex genotyping assay. M, 100-bp ladder molecular weight marker; Lane 1, input 50% HeLa cell pellet, 50% 5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.0; Lane 2, input 10% HeLa cell pellet, 90% 5mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.0; Lane 3, 5% HeLa, 95% 5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.0; Lane 4, 2% HeLa, 98% 5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.0; Lane 5, 1% HeLa cell pellet, 99% 5mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.0; Lane 6, input 50% non-HeLa cell pellet, 50% 5mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.0; Lane 7, 10% non-HeLa cell pellet, 90% 5mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.0; Lane 8, 5% non-HeLa cell pellet, 95% 5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.0; Lane 9, 2% non-HeLa cell pellet, 98% 5mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.0; Lane 10, 1% Non-HeLa cell pellet, 99% 5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.0; Lane 11, PCR positive control (10 ng HeLa gDNA); Lane 12, PCR negative control (no input DNA). The gradient triangles indicate the proportion of cell-pellet extract in the input to the genotyping PCR.