Fig 3.
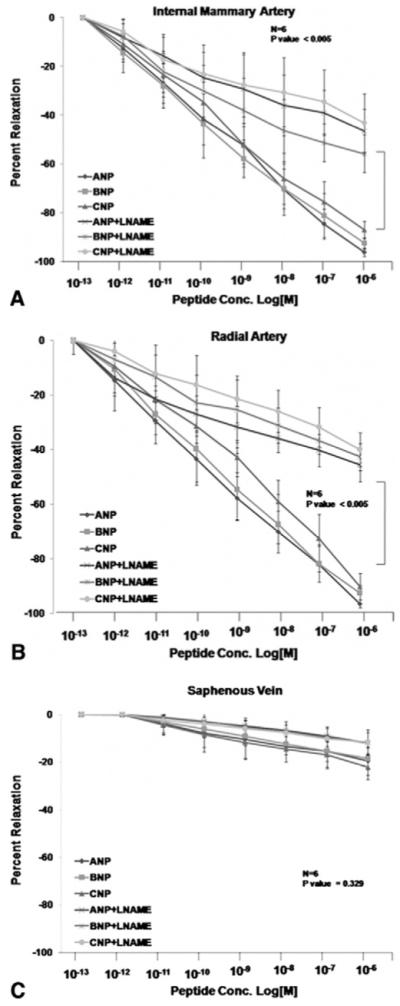
Contribution of nitric oxide synthase to the natriuretic protein response. Segments of internal mammary artery (A), radial artery (B), and saphenous vein (C) were precontracted with U46619 and exposed to the indicated concentrations of natriuretic peptides A, B, or CNP in the presence of the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor L-nitro arginine methyl ester (L-NAME). L-NAME induced modest (yet significant) inhibition of the relaxation response to natriuretic peptides.
