Figure 2.
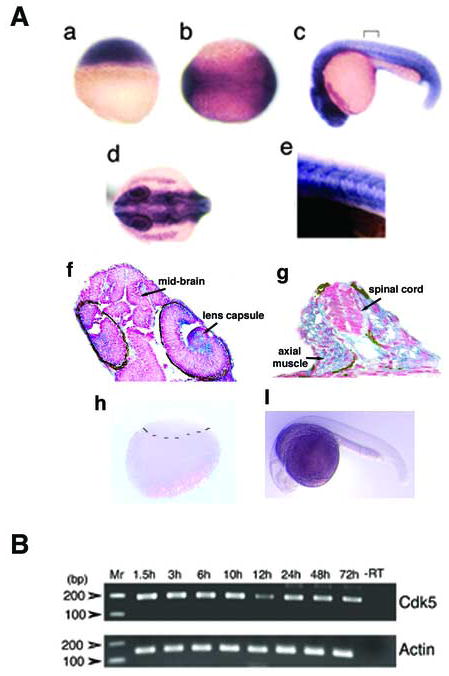
(A) In situ hybridization shows cdk5 expression at 2.5 h after fertilization (hpf) (a), neurula stage at 11.5 hpf (b); 24 h larva, lateral (c) and dorsal views (d). A demarcated region as shown in ‘c’ is magnified 40X (e). A longitudinal section through the anterior region of the 24 hpf embryo shows cdk5 mRNA expression (f) (300 × magnification); and a cross section through the posterior region of the 24 hpf embryo shows cdk5 expression in the spinal cord and axial muscle (g) (400 × magnification). Arrows indicate brain and lens capsule. In situ hybridization assays of blastula (h) and 24 hpf embryo (i) using the cdk5 sense RNA probe are shown. The demarcation in ‘h’ separates the upper blastomeres and lower yolk sac. (B) RT-PCR analyses of cdk5 (upper panel) and β-actin (lower panel) from cDNAs synthesized from the embryos at various stages of development. Molecular markers are shown and the amplification product containing the mRNA from the 72 hpf embryos but no reverse transcriptase is shown (-RT) as a negative control.
