Fig. 1.
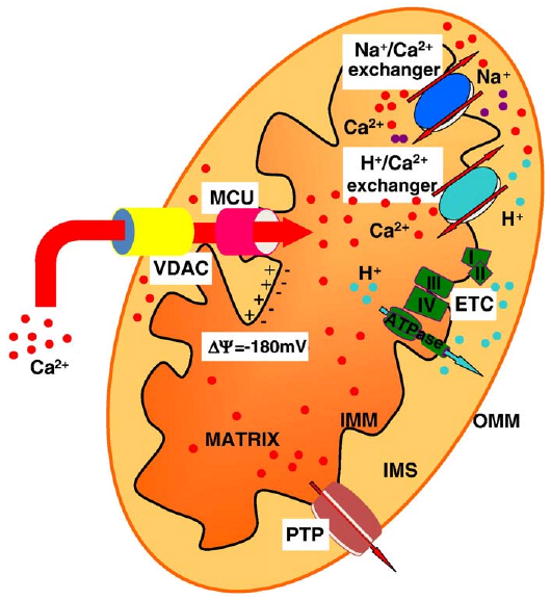
Schematic map of mitochondrial Ca2+ transporters. Mitochondria accumulate Ca2+ in the matrix via an electrogenic Ca2+ uniporter (MCU) that acts to equilibrate Ca2+ according the electrochemical gradient generated by the respiratory chain (ETC). Voltage Dependent Anion Channel (VDAC) controls the Ca2+ diffusion through the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM), thus facilitating mitochondrial Ca2+ accumulation. As to the efflux pathways, a Na+/Ca2+ and a H+/Ca2+ exchangers have been shown to operate. The permeability transition pore (PTP) opening plays different roles: its brief opening could allow rapid Ca2+ release, but its long-lasting openings (potentiated by apoptotic stimuli and Ca2+ itself) could trigger cell death process. IMS, intermembrane space; IMM, inner mitochondrial membrane.
