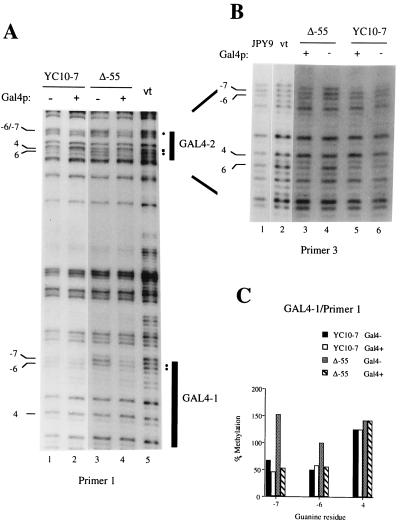
Figure 3.
In vivo footprinting of Gal4p sites on the upper strand. (A) Primer 1: both binding sites GAL4-1 and GAL4-2 are detected and are indicated by black vertical bars. DMS protections are denoted by filled circles on the right side; the respective protected guanines are shown on the left. The hypermethylated G 4 in GAL4-2 is indicated by a filled square. Lanes 1 and 2, YC10-7 in the absence and presence of extra Gal4p, respectively; lanes 3 and 4, Δ-55 in the absence and presence of extra Gal4p, respectively; lane 5, in vitro (vt) control (purified DNA treated with DMS in vitro). (B) Primer 3: detection of GAL4-2. Symbols used are the same as in A. Lane 1, footprint on DNA from the Gal4− strain JPY9; lane 2, in vitro (vt) control; lanes 3 and 4, Δ-55 in the presence and absence of Gal4p, respectively; lanes 5 and 6, YC10-7 in the presence and absence of Gal4p, respectively. (C) Quantitation of the GAL4-1 site shown in Fig. 1A. Shown are residues G −7, −6, and 4 (no changes were observed at position 4). The gel was scanned in a PhosphorImager. Lanes were equalized relative to a “neutral” guanine outside the footprinted region; values were calculated relative to the corresponding residue in the in vitro lane.