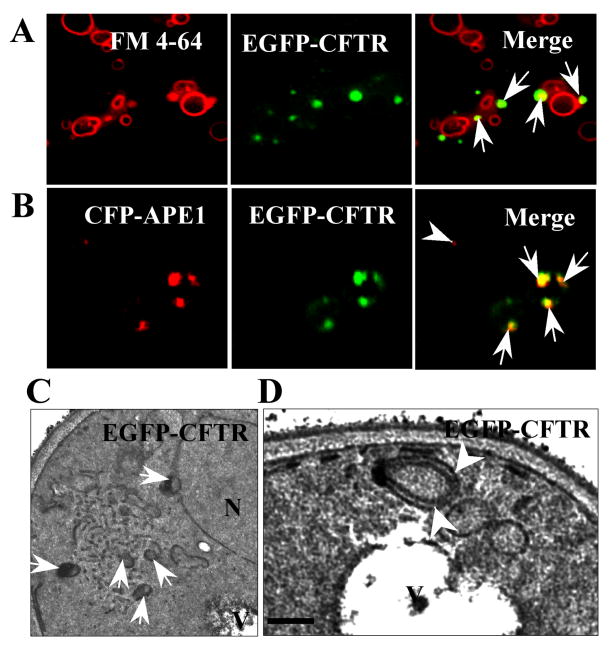
Fig. 4.
Relationship of ERACs to autophagic structures. (A) The EGFP-CFTR ERACs (arrows) are located adjacent to vacuolar membranes stained with FM4-64. Wild-type yeast was induced to form EGFP-CFTR ERACs and stained with FM4-64 followed by fluorescence microscopy. (B) The EGFP-CFTR ERACs are enriched with pre-autophagosomal marker, Ape1p. Wild-type yeast cells were co-transformed with EGFP-CFTR and CFP-APE1 constructs. The cells were then induced with copper for 2 h to form EGFP-CFTR ERACs followed by confocal microscopy analysis. The CFP-Ape1p image was digitally converted to red to enhance visualization. (C, D) Ultrastructure of EGFP-CFTR ERACs. Wild-type yeast cells expressing the EGFP-CFTR were analyzed by electron microscopy. The membranous ERACs are often associated with autophagosome-like structures (C, arrows) and located close to the vacuole (D, arrowheads). Bar: ??? nm.