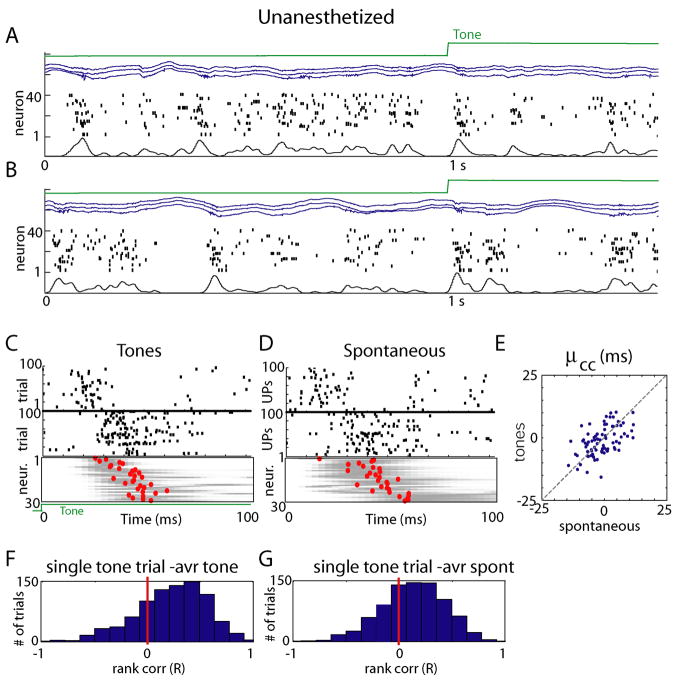
Figure 4.
Preservation of sequential structure between sensory-evoked and spontaneous events in unanesthetized animals. (A, B) Representative raw data plots from an unanesthetized, head-fixed subject in a passive listening paradigm. Again, global fluctuations in activity are seen, although downstates are typically shorter than under anesthesia. (C,D) Similar analysis as in Figure 3B&C, showing preservation of individual neurons’ PETH, and conservation of sequential structure. (E) Conservation of μcc across tones and spontaneous events in unanesthetized animals (similar analysis to Figure 3E). (F,G) Histograms of rank correlations between mean spike times for single tone presentation and average across all tones and spontaneous events respectively.