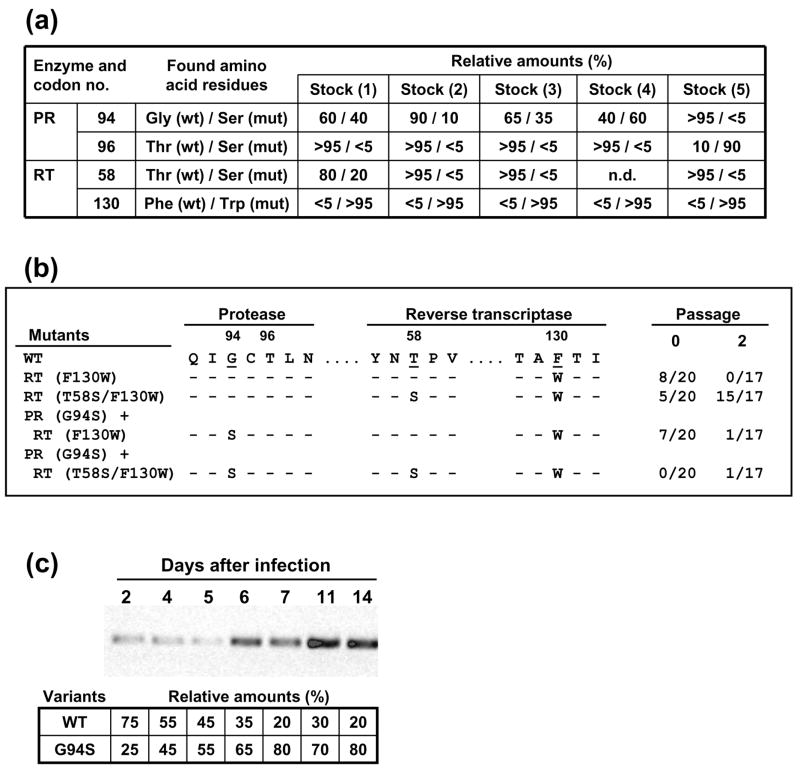
Figure 2.
Emergence of compensatory mutations in the PR-coding region of HIV-189ES061 containing a F130W mutation in its RT-coding region. (a) Sequence heterogeneities in viral stocks derived from transfections of COS-1 cell monolayers, obtained with mutant HIV-1 carrying the amino acid change F130W in the RT-coding region. Numbers indicate the estimated relative percentage of wild-type and mutant virus, as determined after DNA sequencing of the whole viral population. (b) Clonal analysis of HIV variants found in stock 1, before and after two serial passages in MT-4 cells, at a multiplicity of infection of 0.001 TCID50 per cell. The ratios shown on the right indicate the number of clones containing the mutations studied, relative to the total number of clones analyzed. (c) Kinetics of imposition of Ser over Gly-94 in an infection of MT-4 cells (106), using the virus obtained from stock 2, at a multiplicity of infection of 0.0001 TCID50 per cell. RT-PCR was carried out with culture supernatants collected at various days after infection, using primers 198U5U (5′-GTC TGT TGT GTG ACT CTG GT-3′) and 292GD (5′-GAT TGA CTG CGA ATC GTT C-3′). Numbers in the lower panel indicate the relative percentage of virus carrying a mutated (G94S) or a wild-type PR, while maintaining the RT mutation F130W, as determined by DNA sequencing.