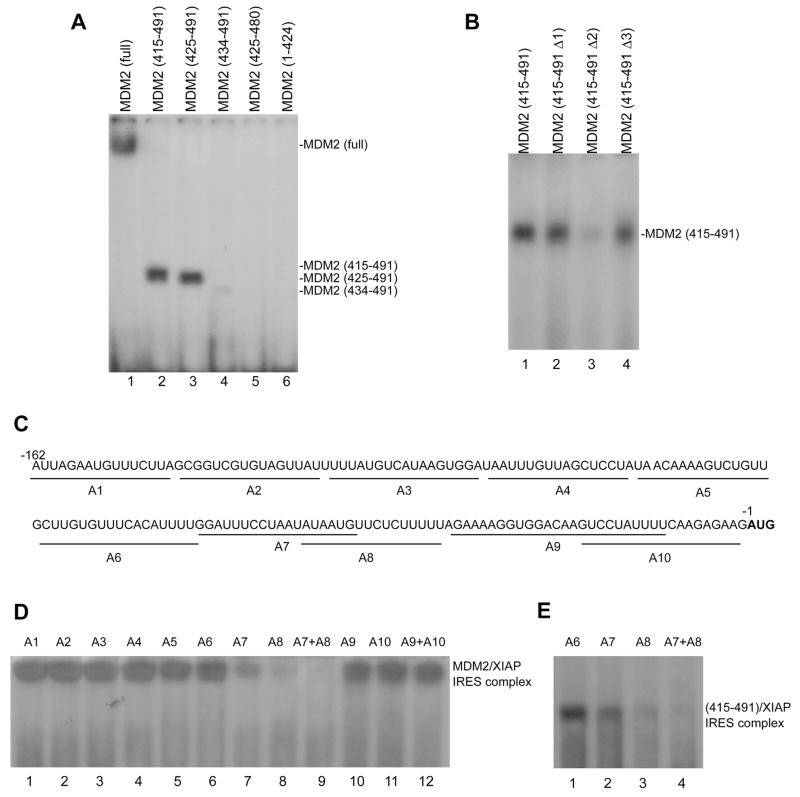
Figure 5.
The C-terminal RING domain of MDM2 binds to the core RNP binding sequence of XIAP IRES. (A) GST-fused full-length MDM2 (lane 1) and different GST-fused MDM2 fragments of the C-terminal RING domain (lanes 2–5) and the fragment with deletion of C-terminal RING domain (lane 6) were incubated with 32P-labeled XIAP IRES (probe 1 in Figure 5); the formation of MDM2 XIAP IRES complexes was detected as described in Figure 5C. (B) UV cross-linking and binding assay similar to (A) for the interaction between XIAP IRES and GST-fused wt (lane 1) and different mutant (lanes 2–4) C-terminal RING domains of MDM2: MDM2 (415–491 Δ1) with a S428G mutation, MDM2 (415–491 Δ2) with a G448S mutation, MDM2 (415–491 Δ3) with a L487S mutation. (C) Mapping the MDM2-binding site within XIAP IRES. Nucleotide sequence of the 162-nt XIAP IRES (probe 1 as described in Fig. 5A) and the positions of antisense (A1–A10) used for binding site mapping are shown under the sequence. The first codon (AUG) is bold. (D) Antisense mapping of the XIAP IRES/MDM2 binding site. Indicated antisense oligonucleotides were annealed to probe 1, then incubated with full-length rhMDM2 and UV cross-linked. The MDM2/XIAP IRES complex was analyzed as described in Figure 5C. (E) Similar antisense mapping of binding within XIAP IRES to the 415–491 fragment containing the C-terminal RING domain of MDM2 protein.