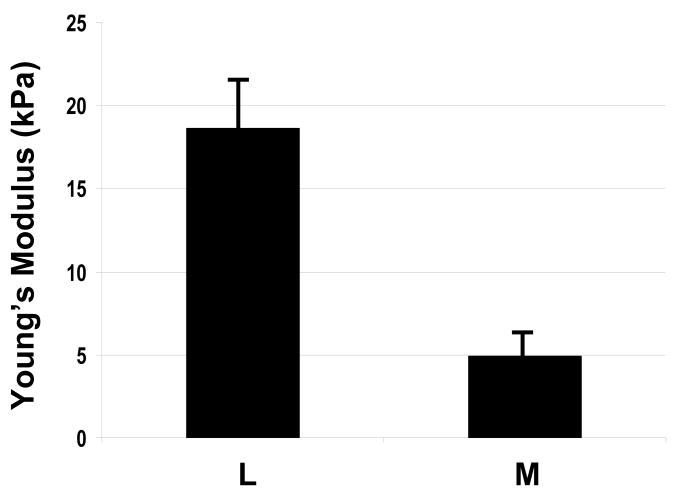
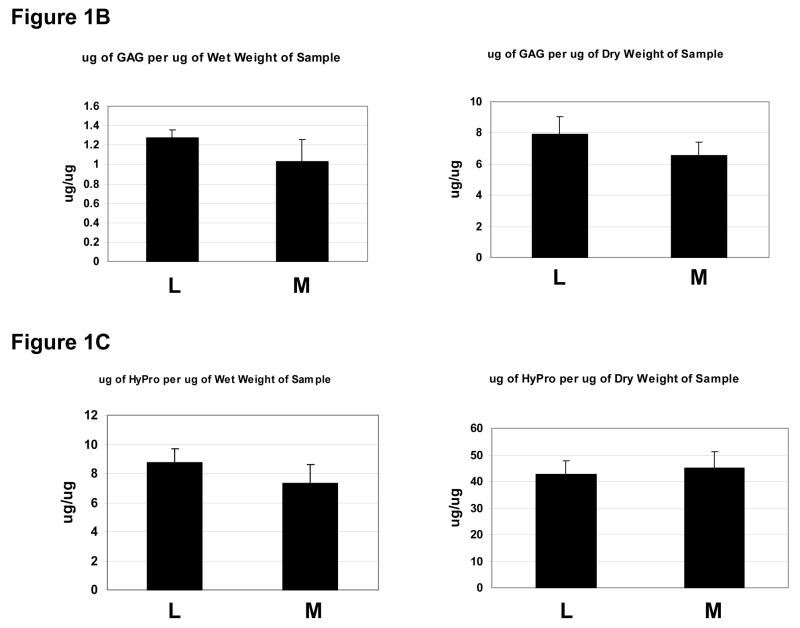
Figure 1. Mechanical testing in matched surgical specimens of uterine leiomyoma and myometrium.
1A: Measurement of compressive resistance to 10% strain (Young’s modulus) in leiomyoma and myometrial samples. Y=kilopascals (kPa), mean±SEM. X=samples of myometrium (M) or leiomyoma (L). Results were replicated in four independent studies.
1B: Measurement of total sulfated GAG content in matched leiomyoma and myometrial samples analyzed by compression using the blyscan method for wet (left panel) and dry weight (right panel). Y axes= micrograms of GAG per microgram of sample. X axes=sample myometrium (M) or leiomyoma (L). Results shown are averages of 3 representative assays.
1D: Hydroxyproline measurement in matched leiomyoma (L) and myometrial (M) samples corrected for wet and dry weight, as shown. Results shown are representative of 3 assays.