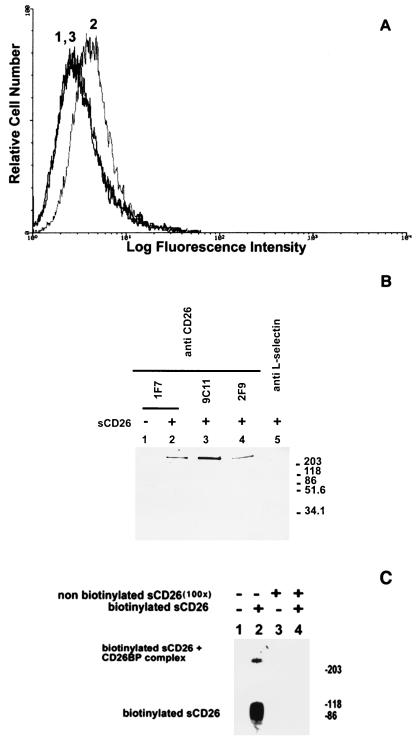
Figure 1.
Binding of sCD26 to cell surface protein p300. (A) Specific binding of sCD26 to cell surface of K562 cells. Cells were stained with phycoerythrin-streptavidin alone (peak 1) or with biotinylated sCD26 and phycoerythrin-streptavidin (peak 2), followed by flow cytometry analysis. Binding of biotinylated sCD26 was inhibited by a 100-fold excess of nonbiotinylated sCD26 (peak 3). (B) Immunoprecipitation of cell surface CD26-binding protein p300. Surface-biotinylated K562 cells were incubated with sCD26 (lanes 2–5) or PBS alone (lane 1) followed by cross-linking with cleavable cross-linker DTSSP (20). sCD26 and its cross-linked complex were immunoprecipitated with three different anti-CD26 antibodies (lanes 1–4) or isotype-matched control antibody (TQ1; anti-l-selectin, lane 5). Immunoprecipitated materials were reduced (to cut cleavable chemical cross-linker) and then analyzed by SDS/PAGE and detected with streptavidin (20). (C) The binding of labeled sCD26 to p300 was inhibited by an excess amount of nonlabeled sCD26. K562 cells were incubated with biotinylated sCD26 (lanes 2 and 4) or PBS alone (lanes 1 and 3) in the presence (lanes 3 and 4) or absence (lanes 1 and 2) of a 100-fold excess of nonbiotinylated sCD26. After cross-linking with noncleavable cross-linker BS3, sCD26 and its cross-linked complex were immunoprecipitated by anti-CD26 antibody (1F7)-conjugated beads. Immunoprecipitated materials were electrophoresed and detected with streptavidin (20).