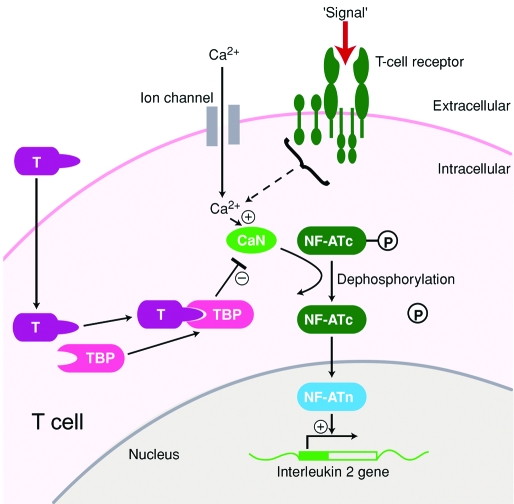
Figure 4.
Mechanism of action of tacrolimus. In the cytoplasm, tacrolimus (T) binds to tacrolimus-binding protein (TBP), forming a tacrolimus–TBP complex, which binds to and blocks calcineurin (CaN). The T–TBP–CaN complex inhibits the activation of the nuclear factor of activated T cells (NF-ATc), thus preventing the entry of NF-ATc into the nucleus. Unable to bind to its nuclear component (NF-ATn), NF-ATc cannot bind to the promoter of the IL2 gene and initiate IL-2 production. T cells therefore will not produce IL2, which is necessary for full T-cell activation. (Modified from reference 28).