Figure 5.
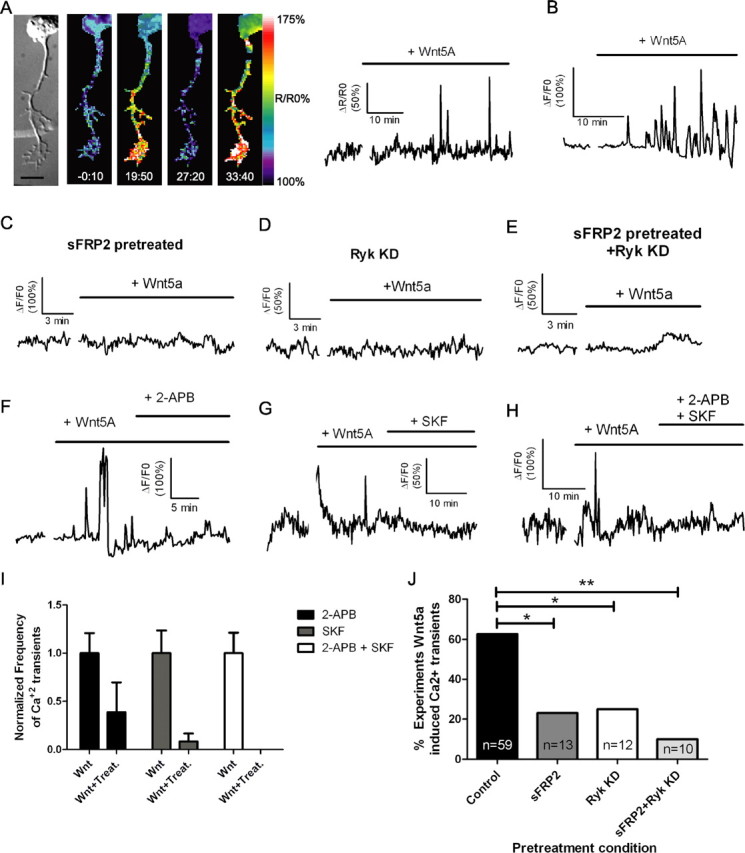
Bath application of Wnt5a to cortical neurons evokes calcium activity through both Ryk and Fz receptors and blocking IP3 receptors or TRP channels attenuates this activity. A, DIC and matching ratiometric fluorescence time-lapse images of a cortical neuron, its axon and growth cone showing calcium activity before (−0:10 min) and after (19:50, 27:20, 33:40 min) the addition of 400 ng/ml Wnt5a. At right, the tracings show increased frequency and amplitude of calcium transients in the cortical neuron shown at left beginning 15 min after addition of Wnt5a. B, Additional example of Wnt5a-evoked calcium activity. C–E, Tracing of calcium activity after application of Wnt5a in the presence of sFRP2 (200 ng/ml) (C) or 2 d after treatment with Ryk siRNA (D) or both (E). F, Tracing of calcium activity evoked by Wnt5a before and after addition of 2-APB (50 μm). G, Tracing of calcium activity evoked by Wnt5a before and after addition of SKF96365 (3 μm). H, Tracing of calcium activity evoked by Wnt5a before and after addition of both 2-APB and SKF96365. I, Quantification of frequencies of calcium transients evoked by Wnt5a before (bars labeled Wnt) and after the addition of calcium channel inhibitors (bars labeled Wnt + Treat.). Frequencies of calcium transients in neurons responsive to calcium channel inhibitors (2-APB, 5/9 neurons; SKF, 4/6 neurons; 2-APB plus SKF, 4/4 neurons) have been normalized to the baseline frequency of calcium transients evoked by Wnt5a before the addition of inhibitors. The absence of a bar in the 2-APB + SKF treatment group indicates that this treatment silenced calcium transients. J, Summary of experiments evoking calcium activity with Wnt5a after treatment with sFRP2 or Ryk siRNA (**p < 0.01, *p < 0.05, Fisher's exact test). n, Number of axons in each condition. Scale bar, 10 μm.
