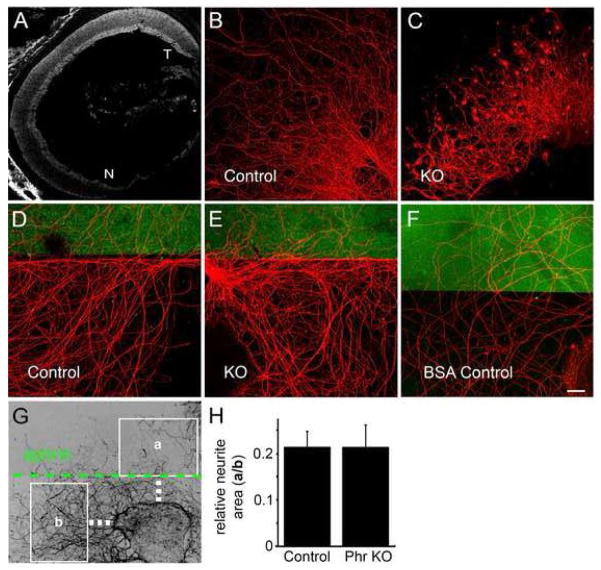
Figure 7.
Mutant axons display morphological defects but respond normally to an ephrin-A border. (A) Retinal EphA gradient is preserved in Phr1 mutants. E18 constitutive Phr1 knockout retina hybridized with recombinant human Ephrin-A5/Fc as described previously (Feldheim et al, 1998). Like control animals, this shows a nasal-temporal Eph receptor gradient in the Phr1 mutant retina (T=temporal, N=nasal). (B,C) Axons from control and constitutive Phr1 knockout retinal explants dissected at E16 and cultured for 14 days, stained with anti-neurofilament. (D,E) Control and constitutive Phr1 knockout RGC axons avoid an Ephrin A2 border (marked in green); explants were dissected at E16, cultured 8 days and stained with anti-neurofilament (red). (F) No border avoidance was seen with a BSA-only border (green) control. (G) Ephrin-A border avoidance was measured as the area of neurites covering a region of ephrin substrate (a) divided by the area of neurites in an equivalent ephrin-free region (b). Quantification is shown in (H). Scale bar = 20 μm.