Figure 2. Schematic model of the role of Bif-1 in autophagy.
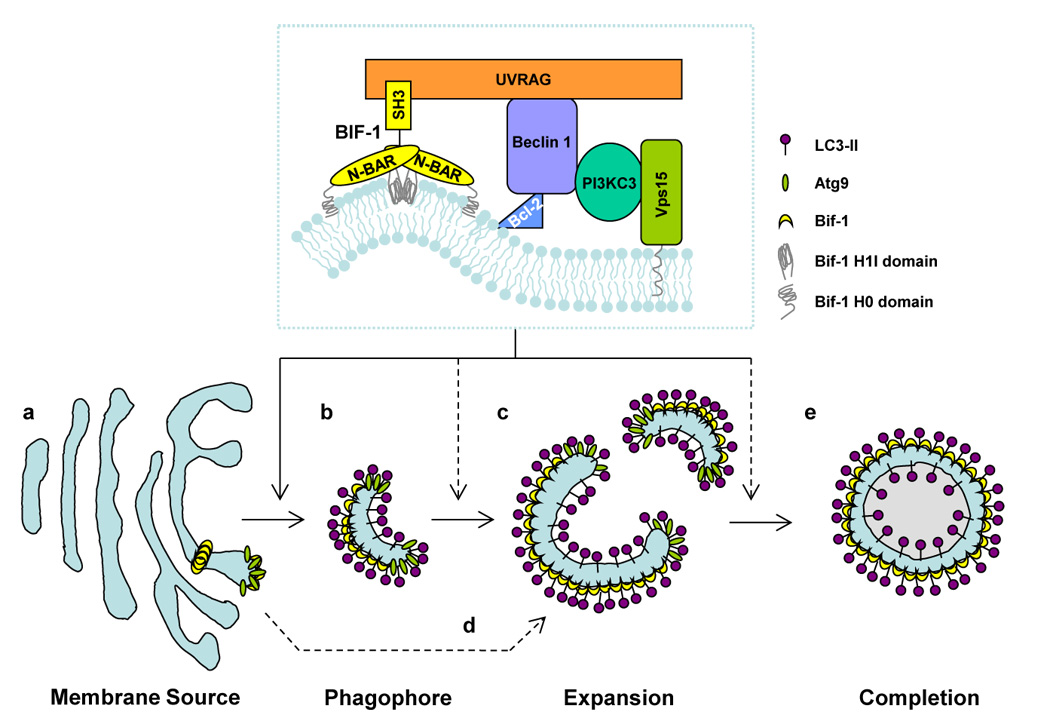
Bif-1 collaborates with PI3KC3 in regulating the biogenesis, expansion and completion of autophagosomes. In response to autophagic signals, Bif-1 tubulates the TGN to generate Atg9-Bif-1-containing vesicles (a). The resultant vesicles serve as the source of phagophores/isolation membranes (b), which are then nucleated and expanded by fusion with other Atg9-Bif-1-containing vesicles (c). Alternatively, Atg9-Bif-1-positive vesicles are delivered to phagophores/isolation membranes, which are de novo synthesized or supplied from unknown donors, as source membranes for the expansion and completion of autophagosomes (d). The membrane is eventually sealed to become a double-membraned autophagosome (e). Atg9 is then released from the vacuole, while Bif-1 remains attached to the autophagosome.
