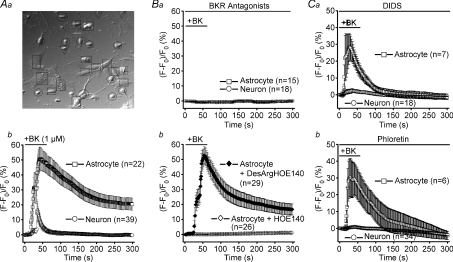
Figure 1. Sensitivity of mouse astrocyte–neuron signalling induced by bradykinin to a B2 receptor antagonist and anion channel blockers.
A, control experiments. a, differential interference-contrast micrograph. Squares, circles and inverted triangles designate responder astrocytes, responder neurons and non-responder neurons, respectively. b, intracellular Ca2+ changes, monitored by the percentage increase in the fluo-4 fluorescence intensity, during and after stimulation with 1 μm bradykinin (BK). The mean peak Ca2+ response in co-cultured astrocytes is not significantly different (P > 0.05) from that in astrocytes cultured alone, whereas that in co-cultured neurons is significantly different (P < 0.005) from that in neurons cultured alone. B, experiments with antagonists of bradykinin receptors (BKR). a, effects of combined application of antagonists of B1 and B2 subtypes of BKR on Ca2+ responses to 1 μm bradykinin (BK) in both astrocytes and neurons in the same co-culture. b, effects of an antagonist of the B2 receptor, 5 μm HOE140, and an antagonist of the B1 receptor, 5 μm[des-Arg10]-HOE140 (DesArgHOE140), on BK-induced Ca2+ responses in astrocytes. The mean peak Ca2+ response in the presence of DesArgHOE140 is not significantly different (P > 0.1) from that in its absence (Ab). C, experiments with blockers of VSOR (a: 200 μm DIDS, b: 100 μm phloretin). The astrocytic Ca2+ responses in the presence of DIDS (a) and phloretin (b) are not significantly different (P > 0.05) from that in the absence of drugs (Ab), whereas the neuronal Ca2+ responses are significantly different (P < 0.005) from that in Ab.