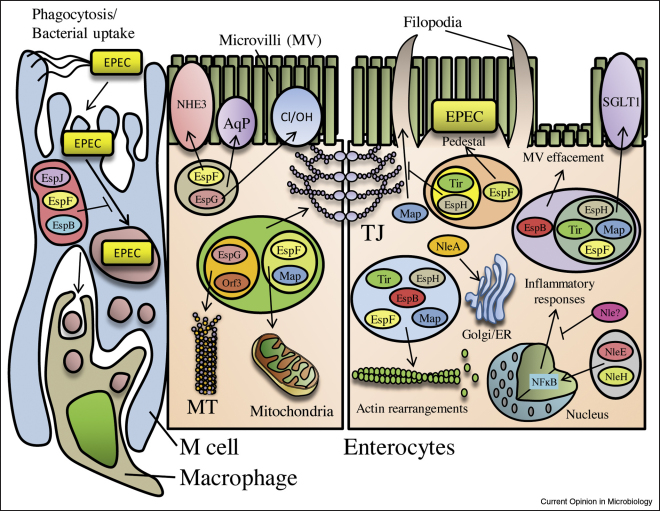
Figure 1.
The complexity of EPEC effector function. The multifunctional and overlapping properties of the EPEC effectors are depicted here by grouping effector functions together. Three effectors have anti-phagocytic activities (shown here using the phagocytic-like gut-associated antigen presenting M-cells) whilst at least five effectors act on microvilli and four inhibit SGLT-1 and other transporter activity, four disrupt tight junctions and three are involved in pedestal and filopodia formation. At least three Nle effectors are also involved in inflammatory pathways. Microtubule and Golgi/ER disruption appears to be specific to EspG/Orf3 and NleA, respectively. Also shown are effectors which have known actin-modulating properties. TJ, tight junctions; MT, microtubules; AqP, aquaporins; NHE3, sodium hydrogen exchanger; Cl/OH, Cl−/OH− transporter; SGLT-1, sodium glucose cotransporter-1; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; MV, microvilli.