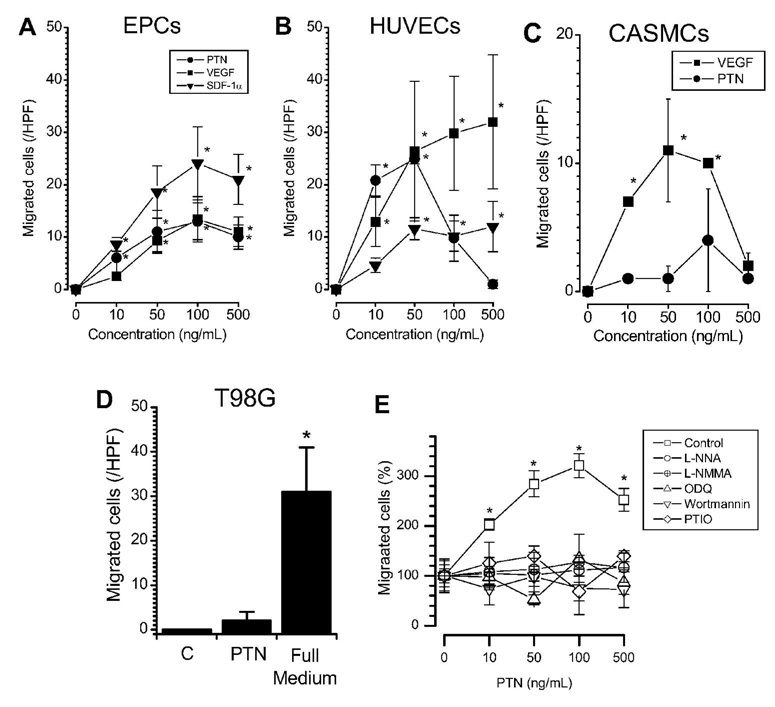
Figure 3. Chemotaxis toward PTN in EPCs.
PTN elicits chemotaxis of EPCs (A, n=5) as compared to other chemokines (VEGF, SDF-1) and (B) to a similar extent as endothelial cells (HUVECs, n=3). In contrast, PTN does not elicit chemotaxis in (C) CASMCs or (D) T98G cells, which have the ability to migrate to VEGF or complete growth medium controls, respectively. Mechanistic inhibitor studies are shown in (E). Chemotaxis of EPCs to PTN is dependent on functional NOS, guanylyl cyclase, and phosphoinositide-3 kinase. * p<0.05 vs. control (repeated measurements ANOVA). Symbols and columns are mean values±SE.