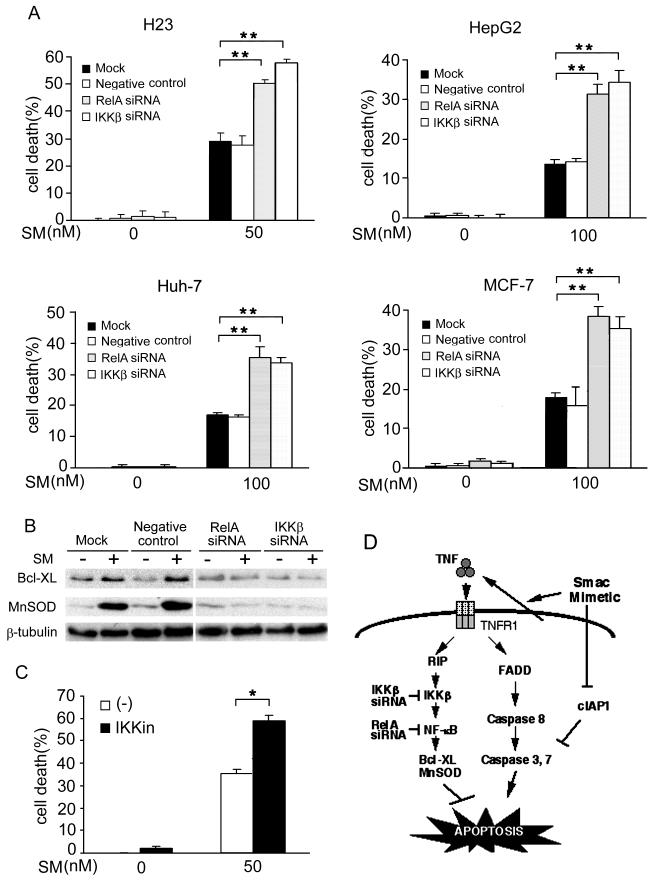
Figure 6. Blocking NF-κB sensitizes SMC3-induced cytotoxicity in cancer cells.
A, H23, HepG2, Huh-7, and MCF-7 cells were mock transfected or transfected with 5 nM of RelA-, IKKβ-, or negative control siRNA. Forty-eight hours after transfection the cells were treated as indicated. Cell death was measured as described in Fig. 1A. **p < 0.01. B, H23 cells were transfected and treated as described in A. BCL-XL and MnSOD were measured by Western blot. β-Tubulin was detected as an input control. C, H23 cells were pretreated with IKK inhibitor II (10 μM) for 1 h followed by SMC3 (50 nM) treatment for 24 h or left untreated. Cell death was measured as in Fig. 1A. *p < 0.05. D, Model of SM-induced NF-κB activation and apoptosis. SM induces apoptosis through suppressing c-IAP1 expression and autocrine TNF. The SM-induced NF-κB activation is mainly through autocrine TNF, which blocks apoptosis. Blockage of the NF-κB pathway by targeting IKKβ or RelA sensitizes SM-induced apoptosis.