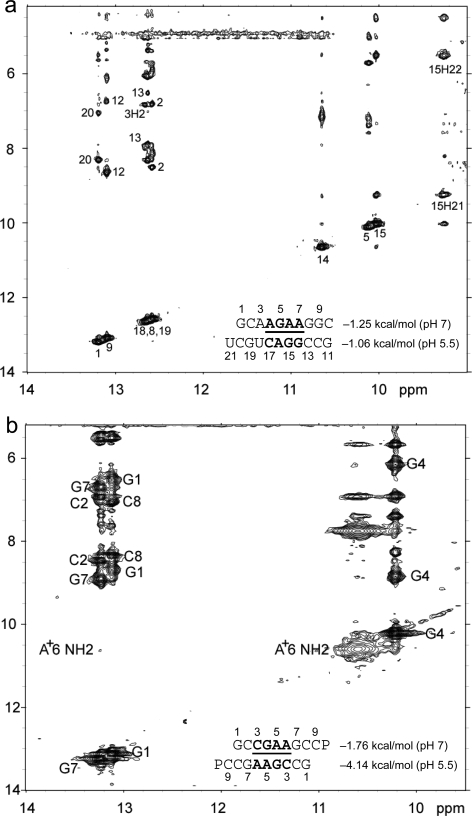
Figure 3.
Two-dimensional exchangeable proton SNOESY spectra (150 ms mixing time in 80 mM NaCl, 10 mM sodium phosphate, and 0.5 mM sodium EDTA). The NOE cross-peaks of G imino protons to C amino and G amino protons are labeled with corresponding residues. Values beside the sequence are ΔG°37,loop in kcal/mol measured in 1 M NaCl at pH 5.5 (bottom) and pH 7 (top). (a) 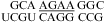 (CT = 0.5 mM, pH 5.3, 0 °C, see Figure 2d for 1D spectrum). There is a very weak cross-peak of G1H1−G19H1 (not shown). The imino protons of G5, G14, and G15 have chemical shifts and cross-peaks typical of consecutive sheared GA pairs (16,20,72). The G15 amino protons resonate at 9.2 and 5.5 ppm, respectively, suggesting the formation of sheared GA pairs with G5 and G15 in the C2′-endo sugar pucker (73,74). There is no indication of the formation of A+C pair in this loop. (b)
(CT = 0.5 mM, pH 5.3, 0 °C, see Figure 2d for 1D spectrum). There is a very weak cross-peak of G1H1−G19H1 (not shown). The imino protons of G5, G14, and G15 have chemical shifts and cross-peaks typical of consecutive sheared GA pairs (16,20,72). The G15 amino protons resonate at 9.2 and 5.5 ppm, respectively, suggesting the formation of sheared GA pairs with G5 and G15 in the C2′-endo sugar pucker (73,74). There is no indication of the formation of A+C pair in this loop. (b) 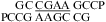 (CT = 1.5 mM, pH 5.1, −5 °C, see Figure 2f for 1D spectrum). The cross-peak of G1H1−G7H1 is unresolved because of overlap but is observed in
(CT = 1.5 mM, pH 5.1, −5 °C, see Figure 2f for 1D spectrum). The cross-peak of G1H1−G7H1 is unresolved because of overlap but is observed in 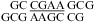 (see and Figure 2e for 1D spectrum). The broad peak at ∼10.6 ppm is likely due to the amino protons of A+6, which shows a strong cross-peak to the other amino proton and a weak cross-peak to the G7 imino proton. Adenine amino protons with similar chemical shift have been observed in other cases of CA+ pairs (12). The G4 amino protons resonate at 8.8 and 6.2 ppm, respectively, suggesting the formation of sheared GA pairs with G4 in the C2′-endo sugar pucker (73,74).
(see and Figure 2e for 1D spectrum). The broad peak at ∼10.6 ppm is likely due to the amino protons of A+6, which shows a strong cross-peak to the other amino proton and a weak cross-peak to the G7 imino proton. Adenine amino protons with similar chemical shift have been observed in other cases of CA+ pairs (12). The G4 amino protons resonate at 8.8 and 6.2 ppm, respectively, suggesting the formation of sheared GA pairs with G4 in the C2′-endo sugar pucker (73,74).