Figure 2.
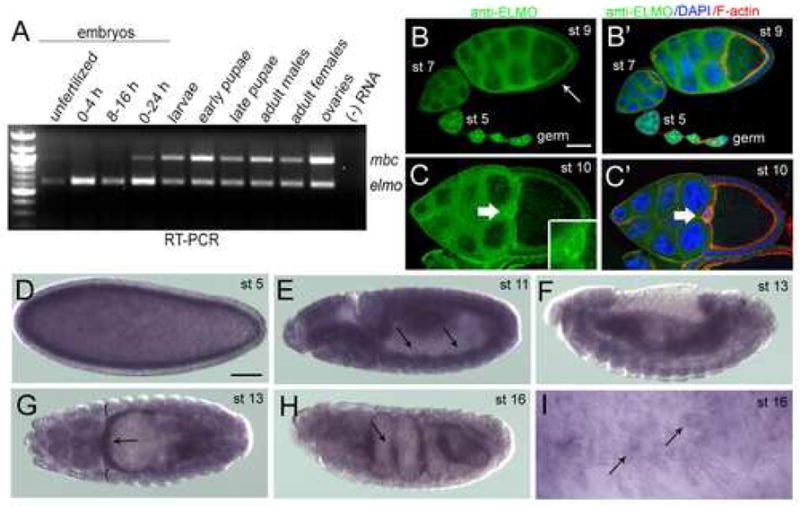
Temporal and spatial expression patterns of elmo. (A) Temporal expression of mbc and elmo transcript by RT-PCR at specific developmental stages in the Drosophila life cycle (B–C′) Immunoreactivity of ELMO antisera in wild-type ovarioles. (B) ELMO is high in the germline at all stages of ovariole development, and is detected in the somatic follicle cells around stage 9 (arrow). (B′) DAPI (blue) and F-actin (red) do not extensively overlap with ELMO (green). (C) ELMO expression is ubiquitous in both the germline and somatic follicle cells of a stage 10 egg chamber, and is especially prominent in the border cells (arrow, inset). (C′) DAPI (blue) and F-actin (red) do not overlap extensively with ELMO (green). (D–I) in situ analysis of elmo in wild-type embryos. (D) elmo is detected at stage 5, suggesting that it is provided maternally. (E) Expression is fairly ubiquitous throughout the embryo, with mesodermal expression (arrows) becoming apparent by stage 11. (F, G) Stage 13 embryo in which expression is broad, but stronger in the gut visceral mesoderm (arrows) than in the somatic mesoderm (brackets). (H) Expression is highest (arrow) in the visceral mesoderm at stage 16. (I) High magnification view of the somatic mesoderm showing elmo expression in the mature muscle. Lateral views are shown in (D–F, H–I) and a dorsal view in G. Scale bar, 50μM
