Abstract
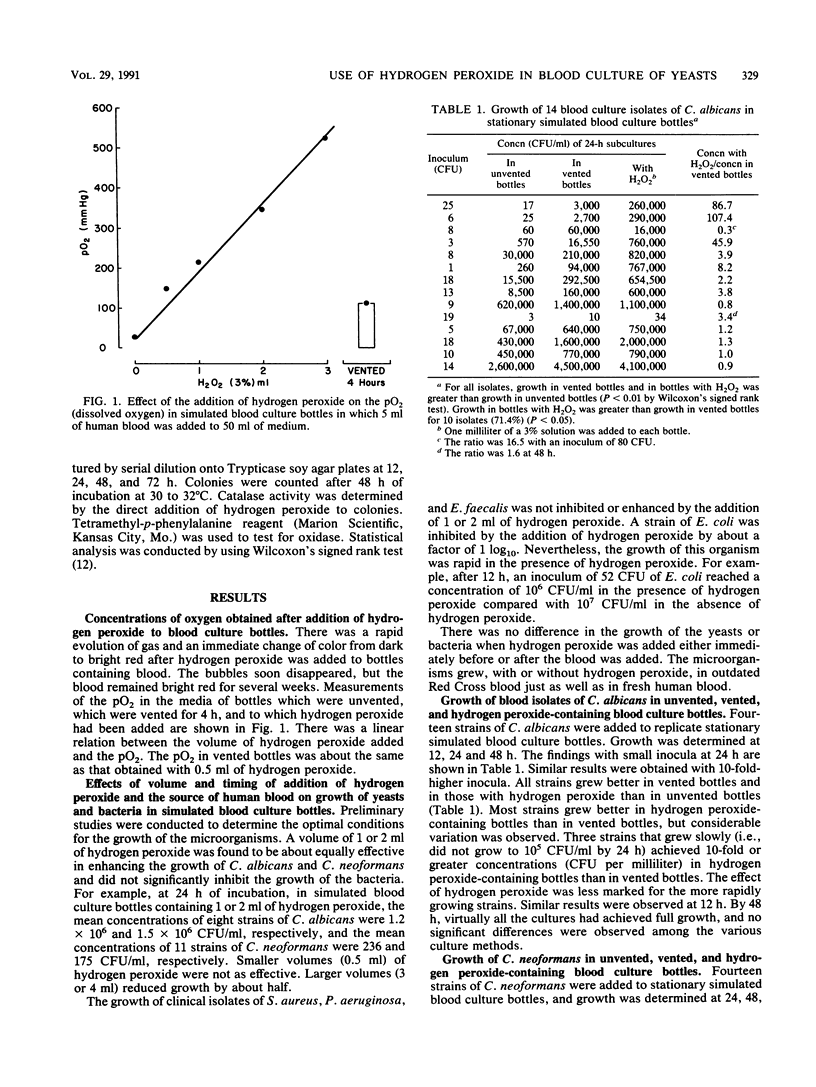
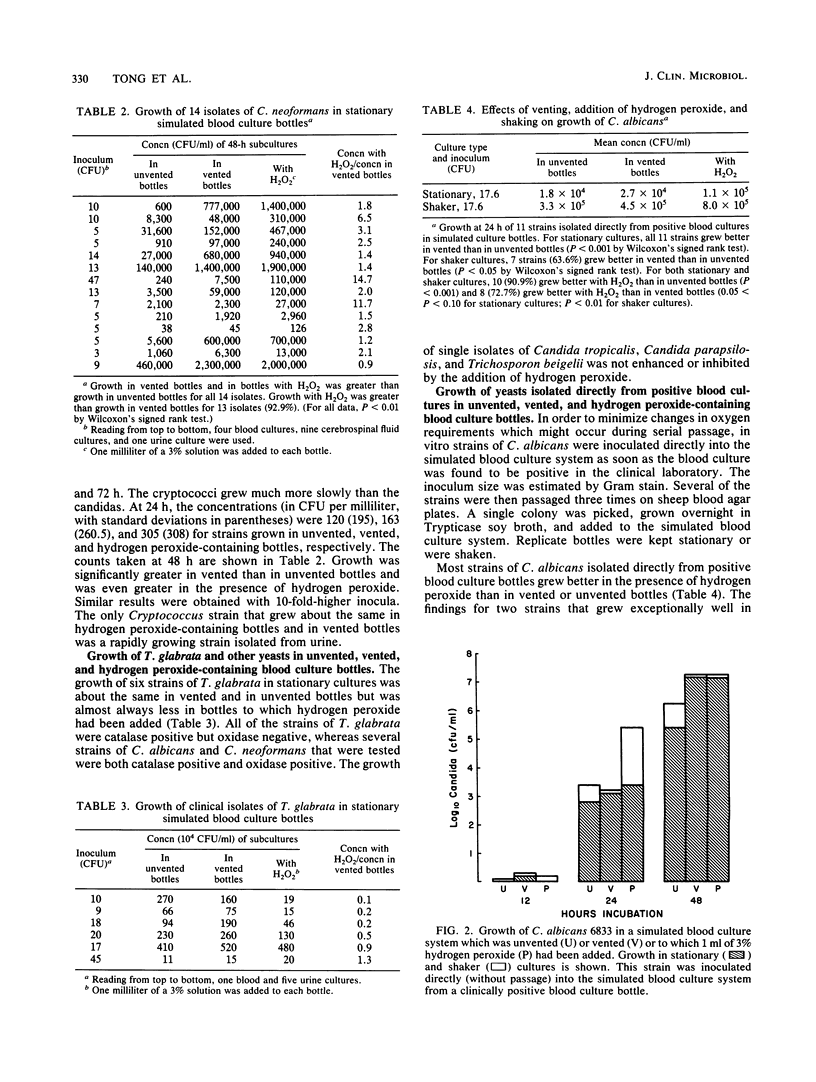
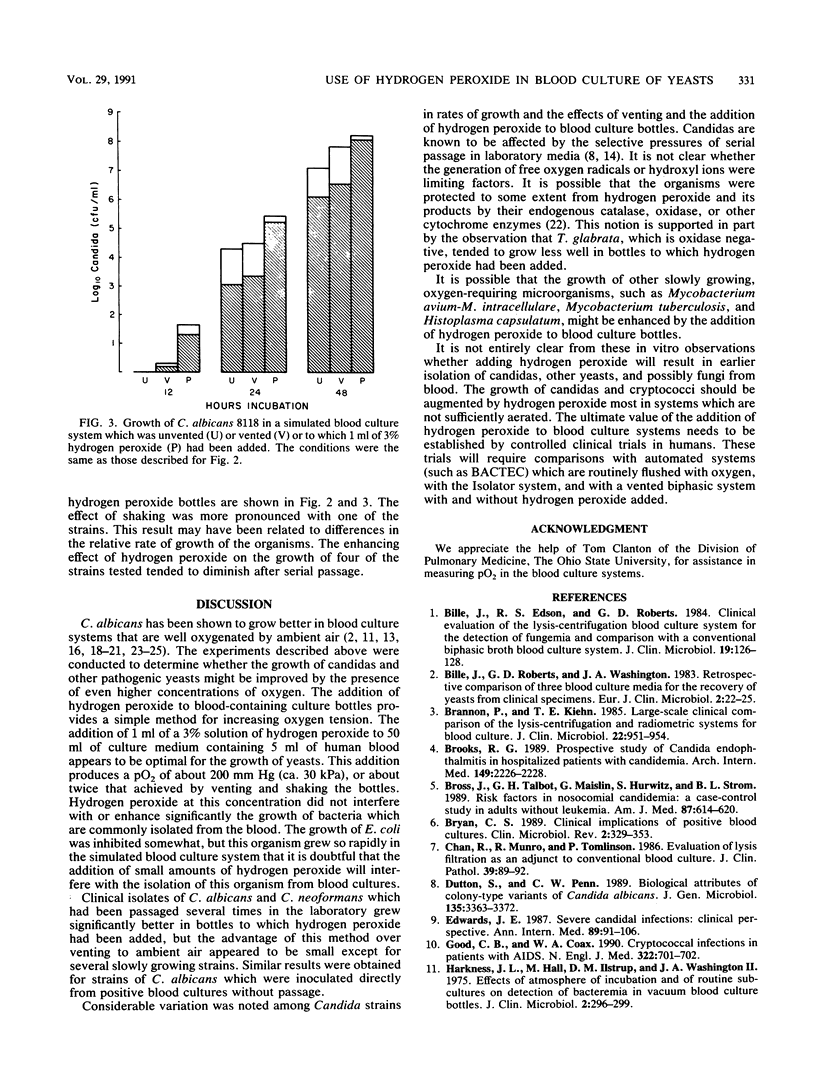
The addition of hydrogen peroxide to blood contained in liquid culture medium increased the dissolved-O2 partial pressure in direct proportion to the volume injected. The effect of hydrogen peroxide on the growth of subcultured clinical isolates of Candida albicans, Cryptococcus neoformans, Torulopsis glabrata, and other yeasts and on the growth of blood culture isolates of representative pathogenic bacteria was compared with its effect on their growth in vented and unvented stationary bottles. C. albicans and C. neoformans grew significantly better in bottles to which hydrogen peroxide had been added than in vented or unvented bottles. The advantage of hydrogen peroxide over venting was most marked with several slowly growing strains. Similar results were obtained in shaker cultures with strains of C. albicans which were inoculated directly from positive blood cultures. The effect of hydrogen peroxide tended to diminish during serial passage. T. glabrata grew less well when hydrogen peroxide was added, perhaps because of the absence of oxidase. The growth of Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterococcus faecalis was not significantly inhibited or augmented by the addition of hydrogen peroxide. The growth of Escherichia coli was inhibited slightly. The value of the addition of hydrogen peroxide to blood cultures to improve the isolation of yeasts needs to be established by a clinical trial which would compare this method with established methods.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bille J., Edson R. S., Roberts G. D. Clinical evaluation of the lysis-centrifugation blood culture system for the detection of fungemia and comparison with a conventional biphasic broth blood culture system. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):126–128. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.126-128.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bille J., Roberts G. D., Washington J. A., 2nd Retrospective comparison of three blood culture media for the recovery of yeasts from clinical specimens. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;2(1):22–25. doi: 10.1007/BF02019918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brannon P., Kiehn T. E. Large-scale clinical comparison of the lysis-centrifugation and radiometric systems for blood culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):951–954. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.951-954.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks R. G. Prospective study of Candida endophthalmitis in hospitalized patients with candidemia. Arch Intern Med. 1989 Oct;149(10):2226–2228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bross J., Talbot G. H., Maislin G., Hurwitz S., Strom B. L. Risk factors for nosocomial candidemia: a case-control study in adults without leukemia. Am J Med. 1989 Dec;87(6):614–620. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(89)80392-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan C. S. Clinical implications of positive blood cultures. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Oct;2(4):329–353. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.4.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R., Munro R., Tomlinson P. Evaluation of lysis filtration as an adjunct to conventional blood culture. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Jan;39(1):89–92. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton S., Penn C. W. Biological attributes of colony-type variants of Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Dec;135(12):3363–3372. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-12-3363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. E., Jr, Lehrer R. I., Stiehm E. R., Fischer T. J., Young L. S. Severe candidal infections: clinical perspective, immune defense mechanisms, and current concepts of therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Jul;89(1):91–106. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good C. B., Coax W. A. Cryptococcal infections in patients with AIDS. N Engl J Med. 1990 Mar 8;322(10):701–702. doi: 10.1056/nejm199003083221017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkness J. L., Hall M., Ilstrup D. M., Washington J. A., 2nd Effects of atmosphere of incubation and of routine subcultures on detection of bacteremia in vacuum blood culture bottles. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Oct;2(4):296–299. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.4.296-299.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. M. Laboratory diagnosis of invasive candidiasis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jan;3(1):32–45. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. J., Rogers A. L., Yancey R. J., Jr Environmental alteration and phenotypic regulation of Candida albicans adhesion to plastic. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3876–3881. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3876-3881.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemieux C., St-Germain G., Vincelette J., Kaufman L., de Repentigny L. Collaborative evaluation of antigen detection by a commercial latex agglutination test and enzyme immunoassay in the diagnosis of invasive candidiasis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):249–253. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.249-253.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz P., Bernaldo de Quirós J. C., Berenguer J., Rodríguez Créixems M., Picazo J. J., Bouza E. Impact of the BACTEC NR system in detecting Candida fungemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):639–641. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.639-641.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prevost E., Bannister E. Detection of yeast septicemia by biphasic and radiometric methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):655–660. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.655-660.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder J. C., Ganguli L. A., Drucker D. B., Keaney M. G., Gibbs A. C. The improved recovery of Candida albicans from fluid culture media. Microbios. 1989;60(243):71–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. D., Horstmeier C., Hall M., Washington J. A., 2nd Recovery of yeast from vented blood culture bottles. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jul;2(1):18–20. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.1.18-20.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. D., Washington J. A., 2nd Detection of fungi in blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Mar;1(3):309–310. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.3.309-310.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenney J. H., Reller L. B., Mirrett S., Weinstein M. P., Wang W. L. Controlled evaluation of the effect of atmosphere of incubation on detection of bacteremia and fungemia in supplemented peptone broth. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):437–442. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.437-442.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verduyn C., Giuseppin M. L., Scheffers W. A., van Dijken J. P. Hydrogen peroxide metabolism in yeasts. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Aug;54(8):2086–2090. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.8.2086-2090.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M. P., Mirrett S., Reimer L. G., Reller L. B. Effect of agitation and terminal subcultures on yield and speed of detection of the Oxoid Signal blood culture system versus the BACTEC radiometric system. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):427–430. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.427-430.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M. P., Mirrett S., Reimer L. G., Reller L. B. Effect of altered headspace atmosphere on yield and speed of detection of the Oxoid Signal blood culture system versus the BACTEC radiometric system. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Apr;28(4):795–797. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.4.795-797.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wey S. B., Mori M., Pfaller M. A., Woolson R. F., Wenzel R. P. Risk factors for hospital-acquired candidemia. A matched case-control study. Arch Intern Med. 1989 Oct;149(10):2349–2353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B., Brauer K. L., Clemens J. R., Beggs S. Effects of gastrointestinal candidiasis, antibiotics, dietary arabinitol, and cortisone acetate on levels of the Candida metabolite D-arabinitol in rat serum and urine. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):283–288. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.283-288.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


