Figure 5.
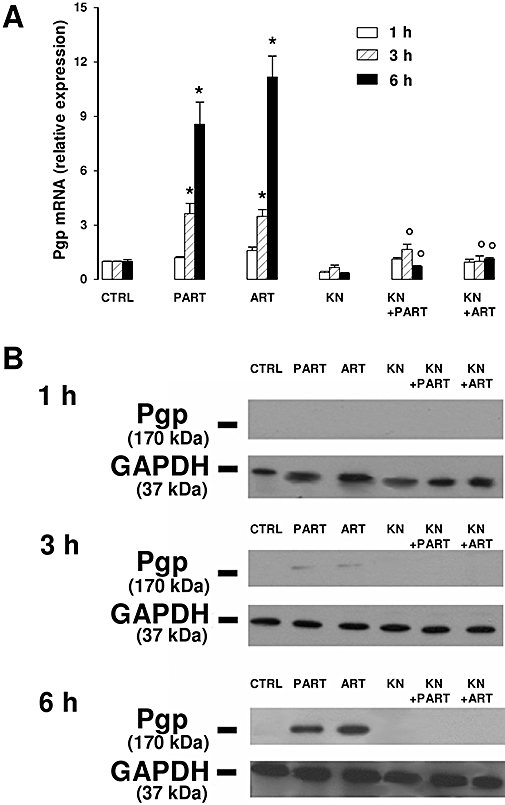
Effect of the CaMKII inhibitor KN93 on Pgp mRNA and protein expression. HT29 cells were incubated for 1 h, 3 h or 6 h in the absence (CTRL) or presence of either parthenolide (PART, 10 µmol·L−1) or artemisinin (ART, 10 µmol·L−1), alone or together with KN93 (KN, 10 µmol·L−1). At the end of the incubation time, cells were subjected to the following investigations. (A) Total RNA was extracted and RT-PCR was performed at 1 h, 3 h and 6 h as indicated in the Methods section. Measurements were performed in triplicate and data are presented as means ± SE (n = 3). Versus CTRL: *P < 0.05. Versus PART or ART respectively: °P < 0.05. (B) Pgp was immunoprecipitated from the whole cellular lysate using an anti-Pgp antibody, then subjected to Western blotting, as described in Methods section. The expression of GAPDH was used as a control of equal protein loading. The Figure is representative of three experiments with similar results. CaMKII, calmodulin-dependent kinase II; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; Pgp, P-glycoprotein; RT-PCR, real-time polymerase chain reaction.
