Figure 7.
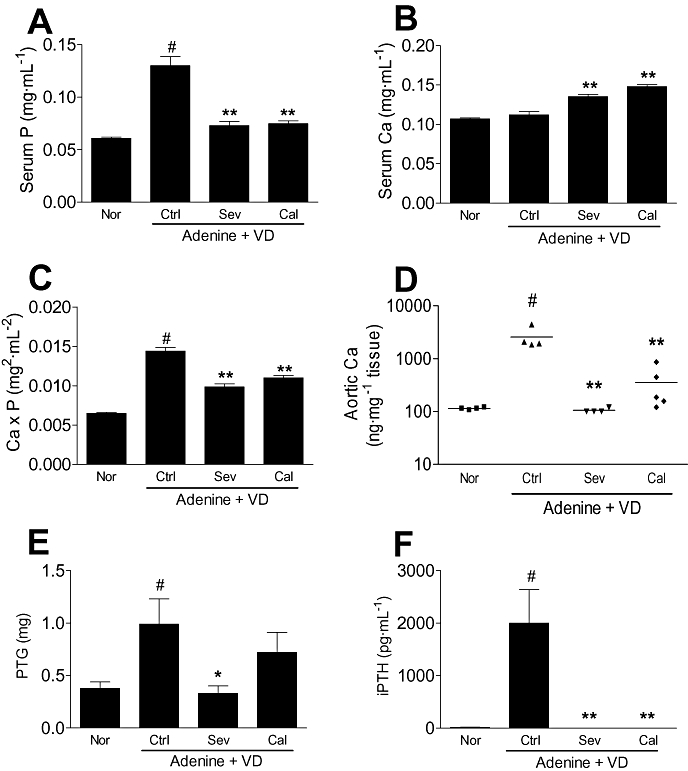
Effects of phosphate binders on active vitamin D3-induced vascular calcification in adenine-dosed rats and on the serum parameters (Exp. 4). Renal failure was induced by 10-day oral administration of adenine at a dose of 600 mg·kg−1, and normal animals were given an MC solution (6 mL·kg−1) instead of the adenine suspension. For 18 days after induction of renal failure, active vitamin D3 (VD; 300 ng·kg−1, 3–4 time week−1) was orally administered to adenine-dosed rats fed with normal powder diets containing 3% MC (n= 4), 3% sevelamer (n= 4) or 3% CaCO3 (n= 5). Normal rats were administered a MC solution instead of active vitamin D3 and fed with a 3% MC diet (n= 4). Sevelamer (Sev) and CaCO3 (Cal) significantly lowered serum phosphate levels (A) and Ca × P products (C), and increased serum Ca levels (B) in adenine-dosed rats given active vitamin D3 orally. Sevelamer inhibited aortic calcification completely and CaCO3 did partially (D). Sevelamer also prevented the hyperplasia of the parathyroid glands (PTG) (E). Both sevelamer and CaCO3 decreased serum iPTH levels to the normal concentration range (F). Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (A, B, C, E, F) or plotted individually (D). Statistical analyses were performed by the Student's t-test for comparison of adenine-dosed control rats and normal rats without active vitamin D3 dosing (#P < 0.05), and among adenine-dosed rats with or without active vitamin D3 dosing by Dunnett's test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). Ca × P, calcium × phosphate; MC, methylcellulose.
