Figure 4.
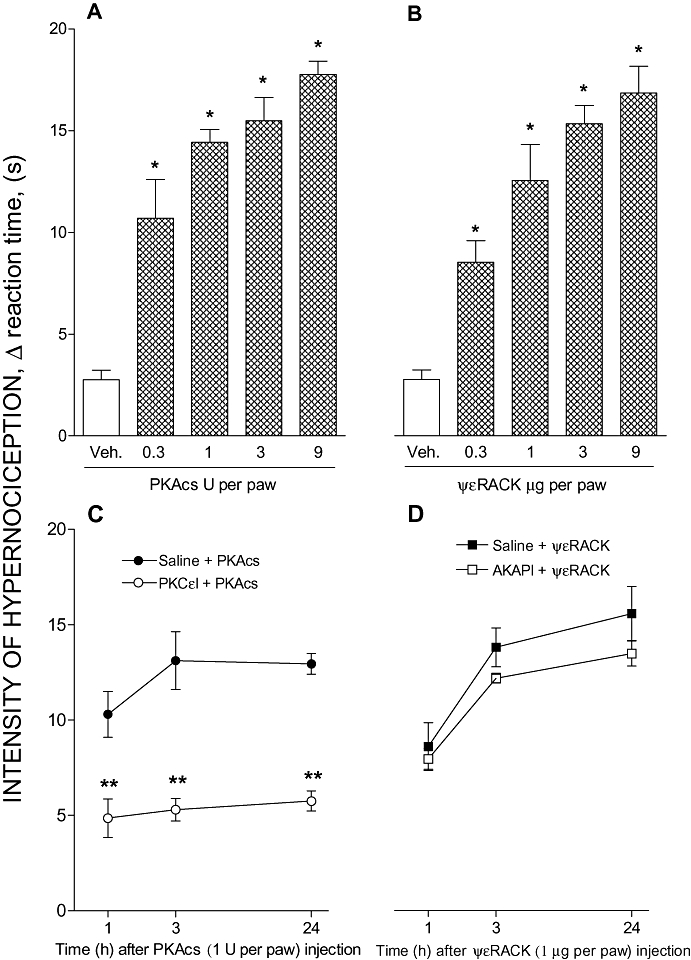
Crosstalk between PKA and PKCε in paw hypernociception. All i.pl. treatments are shown as the dose per paw. Panels (A) and (B): Hypernociceptive effect of the catalytic subunit of PKA (PKAcs) or a specific agonist of PKC (ΨεRACK). PKAcs (0.3, 1, 3 or 9 U) or ψεRACK (0.3, 1, 3 or 9 µg) was injected i.pl. and the intensity of hypernociception was determined 1 h after PKAcs (A) or ψεRACK (B) administration respectively. Panels (C) and (D): The effect of PKC inhibitor (PKCεI) upon PKAcs-evoked hypernociception and of PKA inhibitor (AKAP) upon ΨεRACK-evoked hypernociception. The pretreatment with PKCεI [9 µg; i.pl., panel (C)] or AKAPI [0.3 µg; i.pl., panel (D)] was performed 30 min before PKAcs (1 U; i.pl.) or ψεRACK (1 µg; i.pl.) injections respectively. The intensity of hypernociception was determined 1, 3 and 24 h after PKAcs (C) or ψεRACK (D) injection. The data are the means ± SEM of five animals per group. *P < 0.05 compared with control group i.pl. injected with vehicle (saline, 50 µL). **P < 0.05 compared with PKAcs-control rats treated with saline (50 µL). AKAPI, A-kinase anchoring protein St-Ht31 inhibitor peptide; i.pl., intraplantar; PKA, protein kinase A; PKAcs, catalytic subunit of PKA; PKCε, ε isoform of protein kinase C; ΨεRACK, pseudo receptor octapeptide for activated PKCε, a specific agonist of PKCε; PKCεI, PKCεV1–2 peptide, a selective PKCε inhibitor.
