Figure 4.
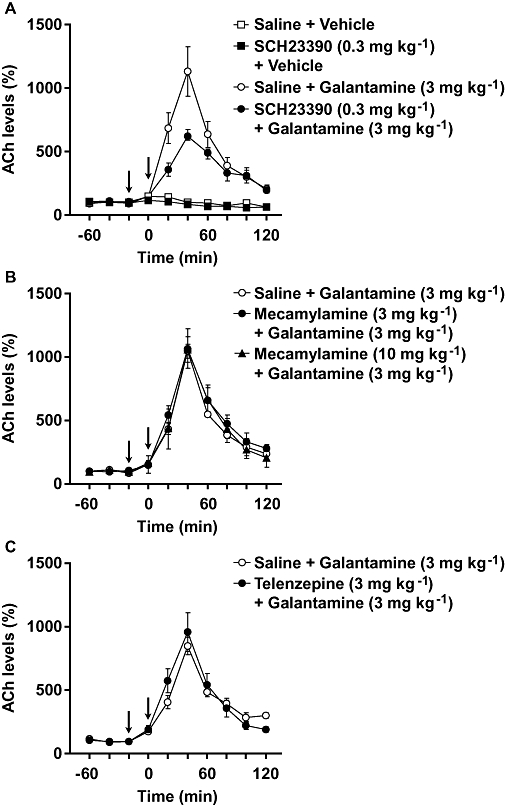
Effects of antagonists of dopamine D1 receptors (SCH23390), nAChR (mecamylamine) and mAChR (telenzepine) on galantamine-induced increase in prefrontal ACh levels in mice. Ringer's solution was perfused without neostigmine in the probe. Galantamine (3 mg kg−1) was injected i.p. at 0 min (right arrow). SCH23390 (0.3 mg kg−1, i.p.) (A), mecamylamine (3 and 10 mg kg−1, i.p.) (B) and telenzepine (3 mg kg−1, s.c.) (C) were injected 20 min before galantamine treatment (left arrow). Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM from 3–4 mice. Repeated measures two-way anova indicated that SCH23390 attenuated galantamine-induced increase in ACh levels, although SCH23390 itself did not affect basal extracellular ACh levels [interaction (treatment × time): F9,54 = 1.214, P > 0.05 and F9,54 = 5.465, P < 0.0001 for basal and galantamine-induced increase respectively]. On the other hand, neither mecamylamine [interaction (treatment × time): F18,72 = 0.261, P > 0.05] nor telenzepine (F9,54 = 0.864, P > 0.05) affected galantamine-induced increase in ACh levels.
