Figure 3.
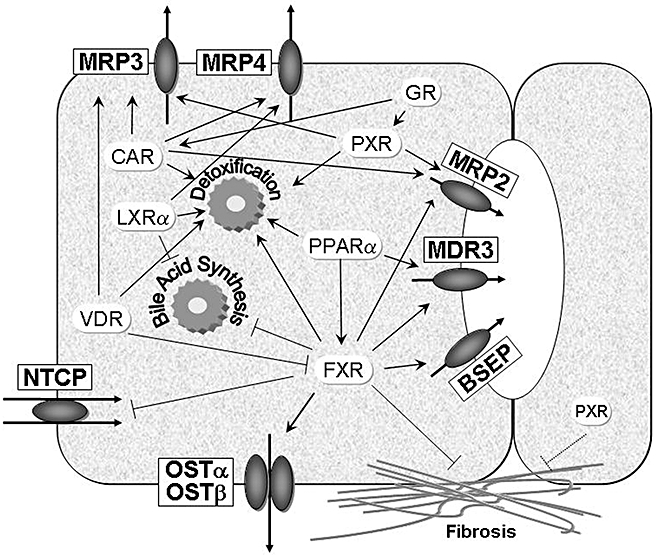
Nuclear receptors as therapeutic targets in cholestasis. Nuclear receptors regulate a large number of target genes mediating transport, synthesis and detoxification of biliary constituents including bile acids. This figure summarizes the anti-cholestatic properties of nuclear receptors that can be targeted therapeutically by synthetic and natural ligands. As indicated in the figure, nuclear receptors regulate overlapping sets of target genes. This may be of relevance, when expression of one nuclear receptor is low due to disease state (as observed in cholestasis). In addition, nuclear receptors may directly regulate fibrogenesis Arrows indicate stimulatory effects, the other lines indicate suppressive effects on target genes. BSEP, bile salt export pump; CAR, constitutive androgen receptor; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; GR, glucocorticoid receptor; LXR, liver X receptor; MRP, multidrug resistance-associated protein; NTCP, Na+/taurocholate cotransporter; OST, organic solute transporter; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; PXR, pregnane X receptor; VDR, vitamin D receptor.
