Figure 3.
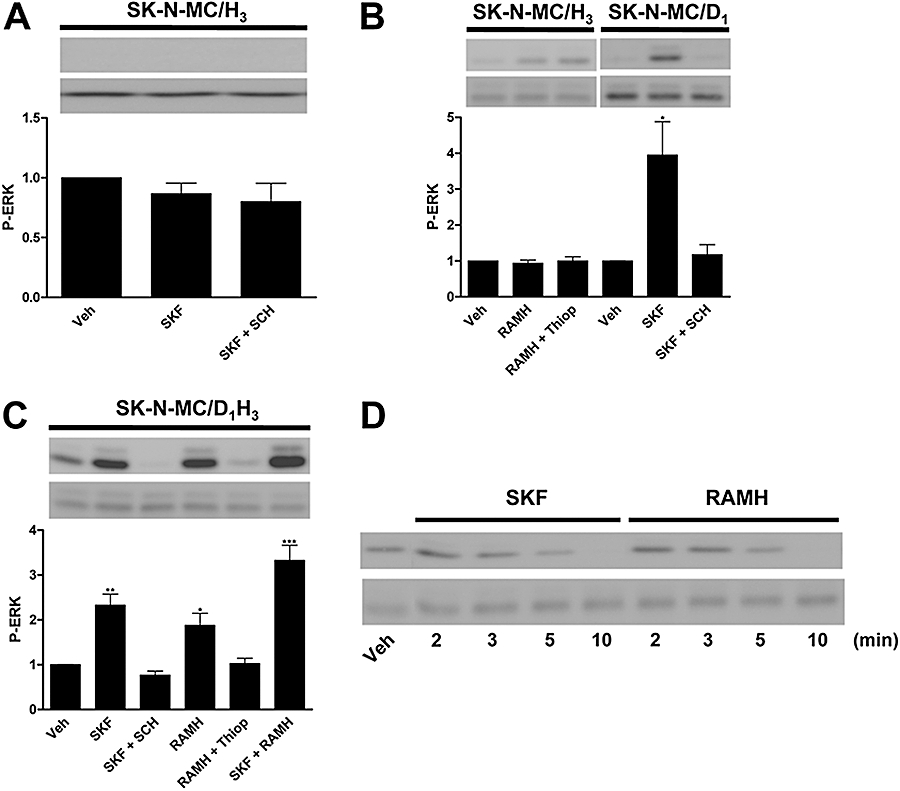
ERK1/2 phosphorylation (P-ERK) via the D1–H3 receptor heteromer in human neuroblastoma cells. SK-N-MC cells expressing H3 receptors (SK-N-MC/H3) or D1 receptors (SK-N-MC/D1) or both (SK-N-MC/D1H3) were treated with the H3 receptor agonist, RAMH (1 µmol·L−1), or with the D1 receptor agonist, SKF 81297 (1 µmol·L−1, SKF) alone or in combination, in the presence or in the absence of the H3 receptor antagonist, thioperamide (10 µmol·L−1, Thiop) or the D1 receptor antagonist, SCH 23390 (10 µmol·L−1, SCH). ERK1/2 phosphorylation was determined as indicated in Methods after 2 min of agonist treatment (A, B and C). In (D) a time–course response of ERK1/2 phosphorylation induced by 1 µmol·L−1 SKF 81297 or 1 µmol·L−1 RAMH in SK-N-MC/D1H3 cells is shown. A representative Western blot is shown in each panel. The immunoreactive bands from three to four experiments were quantified, and values represent the mean ± SEM of fold increase of phosphorylation over the basal levels found in untreated cells. Significant differences were calculated by Student's t-test for unpaired samples (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; RAMH, R-α-methyl histamine; Veh, vehicle.
