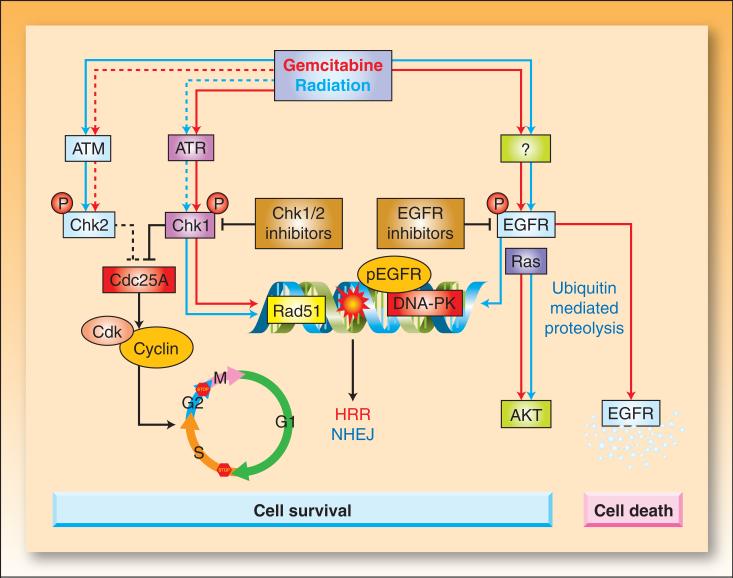
Figure 3. The effects of gemcitabine and radiation on cell cycle checkpoints and EGFR signaling.
Radiation-induced double strand breaks or gemcitabine-induced replication stress trigger the activation of ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) and ATM and Rad3-related (ATR) kinases, respectively (92). Active ATM/ATR phosphorylate and activate Chk1 and Chk2 (93-95) which phosphorylate Cdc25 phosphatases, leading to their inactivation through degradation (Cdc25A) or cytoplasmic sequestration (Cdc25C) (93, 96). In the absence of Cdc25 phosphatase activity, cyclin dependent kinases (Cdk1 and Cdk2) remain bound by inhibitory phosphorylations, resulting in arrest of the cell cycle at G1/S, intra-S, or G2/M. Treatment of cells with gemcitabine prior to radiation results in radiosensitization that can be attributed to a number of events (Box 1), including dATP depletion and S-phase arrest. Inhibition of Chk1 sensitizes cells to gemcitabine and radiation by a number of potential mechanisms including abrogation of cell cycle arrest, premature mitotic entry, and inhibition of Rad 51 focus formation resulting in impaired homologous recombination repair (HRR).
EGFR is phosphorylated in response to radiation or gemcitabine by an unknown mechanism(s) (97). Radiation triggers translocation of EGFR into the nucleus (58, 60). This process coincides with transport of Ku70/80 and protein phosphatase 1 into the nucleus, resulting in increases in DNA-PK, repair of DNA-strand breaks (NHEJ; nonhomologous endjoining), and cell survival. Activation of EGFR in response to gemcitabine can also result in activation of the survival signal AKT (46). Activating Ras mutations can result in activation of Ras-dependent pathways, such as PI3K/AKT, even in the presence of EGFR inhibitors. EGFR inhibitors prevent gemcitabine and/or radiation-mediated EGFR signaling and are thought to impair cell survival signals and DNA repair. EGFR inhibition blocks nuclear transport of EGFR and DNA-PK activity (60, 98). In some instances, phosphorylation of EGFR by gemcitabine promotes ubiquitination of the receptor leading to degradation along a proteosome/lysosome pathway (63). EGFR degradation results in down-regulation of the survival signal pAKT, leading to apoptosis. Blocking EGFR degradation at various steps of this pathway reduces gemcitabine-mediated cytotoxicity. Whether an EGFR-activating insult leads to cell survival or cell death may ultimately be determined by the severity and duration of the stress. The colored arrows indicate the effects mediated by gemcitabine (red) versus radiation (blue). Dotted lines indicate less pronounced effects.