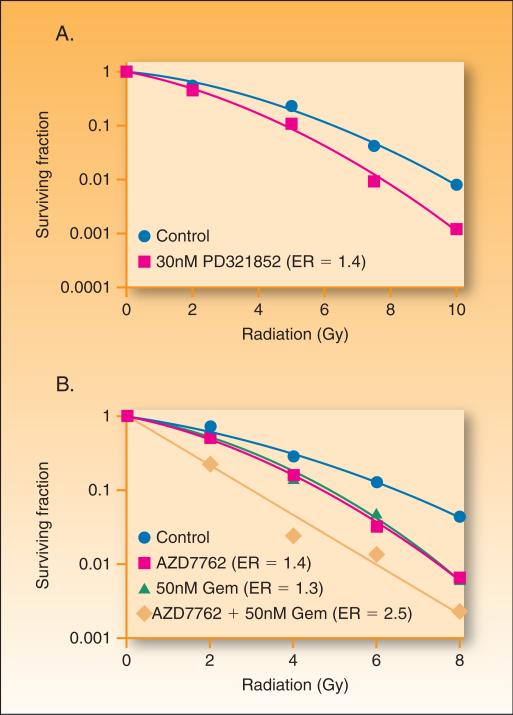
Figure 4. The effects of Chk1 inhibition on radiation and chemoradiation sensitivity.
MiaPaca-2 cells were treated with 30 nM PD-321852 for 24 hrs pre- and post-ionizing radiation (0 −10 Gy) (A) or for 2 hours with gemcitabine (50nM) and then with AZD7762 (100nM) for 1 hour pre- and 24 hours post-irradiaiton (B). Cells were then plated at cloning densities and grown for 10 days to determine the surviving fraction, which represents the fraction of cells surviving radiation treatment relative to un-irradiated controls. Cell survival curves were then fitted using the linear quadratic equation, and the mean inactivation dose was calculated according to the method of Fertil et al. (99). The radiation enhancement ratio was calculated by dividing the mean inactivation dose under control conditions by the mean inactivation dose of Chk1 inhibitor-treated cells.