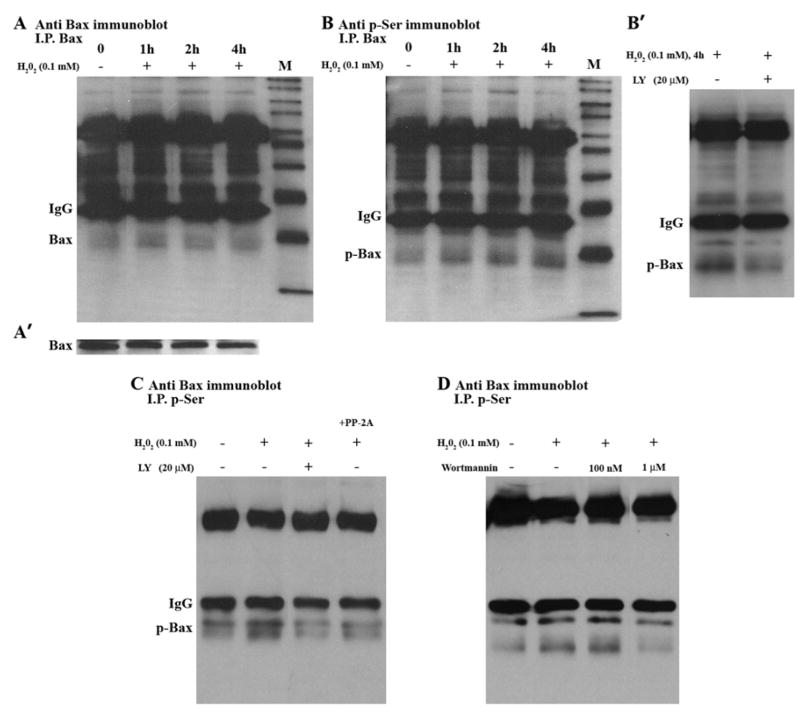
Fig. 3.
Bax phosphorylation in SH-SY5Y Cells. (A) Cells were treated with H2O2 for the indicated times. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Bax antibody (I.P.Bax) and then immunoblotted with Bax antibody. (A′) Whole cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting, using Bax antibody. (B) Cells were treated with H2O2 for the indicated times. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Bax antibody (I.P.Bax) and then immunoblotted with anti-phosphoserine antibody. (B′) Cells were pre-treated with or without LY, and then treated with H2O2 for 4 h. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with Bax antibody and then immunoblotted with anti- phosphoserine antibody. (C) 24 h time course; Cell lysates from control (no treatment), H2O2 alone, LY + H2O2, and H2O2 + PP-2A/C were immunoprecipitated with anti- phosphoserine antibody, and then immunoblotted with Bax antibody. (D) Cells were pre-treated with or without Wortmannin (W), and then treated with H2O2 for24 h. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti- phosphoserine antibody and then immunoblotted with Bax antibody.