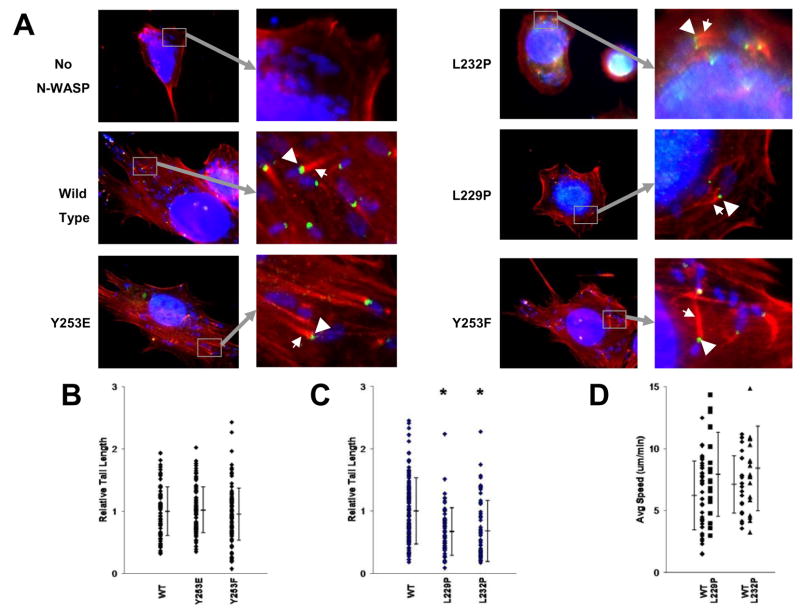
Fig. 2. NWASP regulatory mutants localize appropriately and support Shigella-mediated actin based motility.
(A) Stable cell lines expressing each of the NWASP constructs were infected with Shigella. Cells were stained for DNA (blue), NWASP (green), and actin (red). Insets show polar NWASP localization (arrow heads) and actin tail formation (arrows). (B) Tails formed in cells expressing NWASP Y253E and Y253F are similar in length to those expressed in cells expressing WT NWASP. (C) Tails formed in cells expressing NWASP L229P and L232P are shorter in length than those expressed in cells expressing WT NWASP. * P<.05 (Mann-Whitney test). (D) Time lapse microscopy was used to quantify the velocity of Shigella undergoing actin-based motility. Average speed of Shigella in cells expressing WT NWASP, L229P, or L232P is shown.