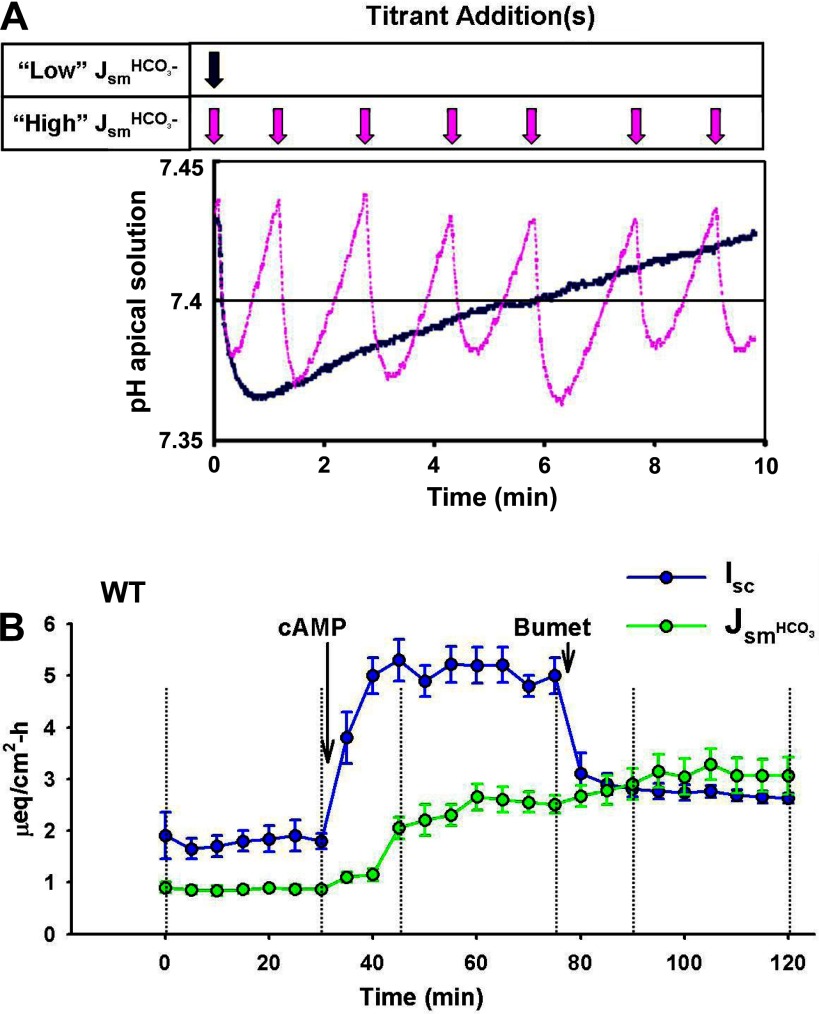
Fig. 10.
A: changes in pH of an unbuffered luminal solution during pH stat measurements of fast and slow rates of HCO3− secretion. Traces showing changes in pH of the luminal solution during pH stat studies. Note the pH excursions about the target pH 7.4 (solid line) for an epithelium with high HCO3− secretory flux (Jsm) (pink trace and arrows) and low HCO3− secretory flux (blue trace and arrow). [Modified from Krouse et al. (24).] B: pH stat measurements of HCO3− secretion (JsmHCO3−) and Isc across WT murine duodenum during sequential treatments with forskolin (cAMP; 10 μM, mucosal and serosal addition) and bumetanide (Bumet; 50 μM, serosal addition). Compare the rapid increase in Isc (blue line and symbols) with the slower changes in JsmHCO3− (green line and symbols) after cAMP treatment. The different time courses for Isc and JsmHCO3− demonstrate the lag in pH measurement attributable to mixing of the superfusate. Bumetanide treatment inhibits Cl− secretion and reduces the Isc without affecting the JsmHCO3−. Vertical dashed lines indicate 3 successive steady-state flux periods (30 min each). n = 5–7 duodenal preparations.