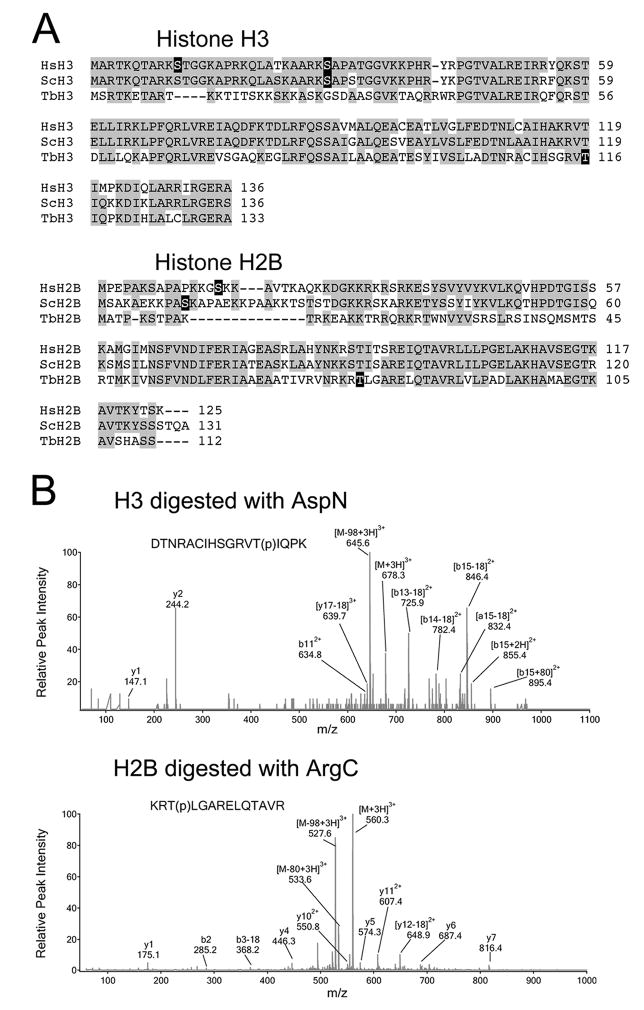
Fig. 4.
Identification of phosphorylation sites within TbH3 and TbH2B.
(A) Sequence alignments of histone H3 and H2B from human (Hs), yeast (Sc) and T. brucei (Tb). Phosphorylation sites are blocked in black.
(B) LC/MS/MS spectra of the triply-charged phosphorylated peptides detected in TbH3 and TbH2B. TbH3 digested with AspN endopeptidase. Peptide DTNRACIHSGRVT(p)IQPK (amino acids 104–120) had a mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of 678.3. The MS/MS spectrum revealed multiple fragment ions including neutral loss fragments [M-H3PO4+3H]3+ at m/z 645.6. Wild-type b112+ was detected, together with [b13-18]2+, [b14-18]2+, [b15-18]2+ and [b13+18]2+. The b-ion series indicated that the phosphorylation occurred at Thr116. TbH2B was digested with ArgC endopeptidase. Triply charged peptide KRT(p)LGARELQTAVR (amino acids 164–177) appeared at 560.3 in the MS scan. The MS/MS spectrum revealed several fragment ions including [M-H3PO4+3H]3+ at m/z 527.6, and y4, y5, y6, y7, y112+, [y12-18]2+. The MS/MS data demonstrated that Thr166 was phosphorylated.