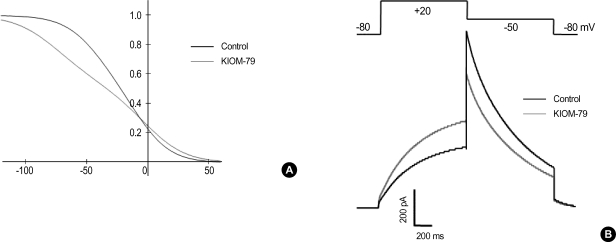
Fig. 6.
Computer simulation of the effects of KIOM-79 on the voltage-dependence of hERG channel activity. (A) A proposed change in voltage-dependence of steady-state inactivation of hERG to reproduce the effects of KIOM-79 on hERG current in Fig. 4. In order to reduce the slope of the voltage-dependence of steady-state inactivation, the opening and closing rate constants were modified as follows. αh=1.0/{1.6*exp([Vm-10]/17.0)+0.7*exp([Vm-10]/300.0)}; βh=1.0/{0.067*exp(-[Vm+30]/17.0)+0.63*exp(-[Vm+30]/150.0)}. The voltage-dependence of opening rate constant was shifted to the right by 10 mV, while that of closing rate constant was shifted to the left by 30 mV. Note that the voltage-dependence shows a deviation from typical Boltzman distribution since there are two exponential terms in the equations describing αh and βh. (B) Reconstructed hERG currents from the altered rate constants of inactivation. Altered inactivation increased the amplitude of membrane current activated by a depolarizing step from -80 mV to +20 mV, whereas it reduced the amplitude of membrane current activated by a repolarizing step from +20 to -50 mV.