Figure 1.
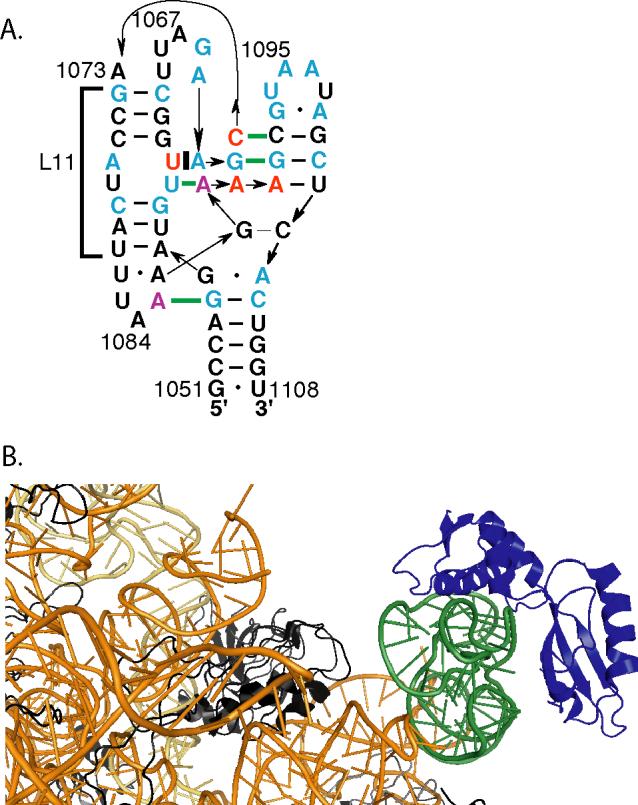
A, Schematic of the L11BD RNA. Nucleotides mutated in this study are indicated in red (U1061 and AA1089−1090, stabilizing) or purple (A1085, A1088, and C1072, destabilizing). Cyan bases are conserved in greater than 97% of bacterial, archaeal, and eukaryotic sequences (15). Of particular importance to this study, at position 1061 only U is found in bacteria, G among the eucarya, but all four bases in archaea (28). The two nucleotide sequence at 1089−1090 is either AA or GU in nearly all organisms. Base-base tertiary interactions are indicated by horizontal thick green lines. The segment of distorted minor groove contacted by L11 is indicated by a bracket. B, View of the Escherichia coli 50S subunit (5) illustrates that L11BDL11 complex is an independent domain isolated from the remainder of the ribosome. L11, blue; other proteins, black; nucleotides 1051−1108 (L11BD), green; 23S RNA, gold.
