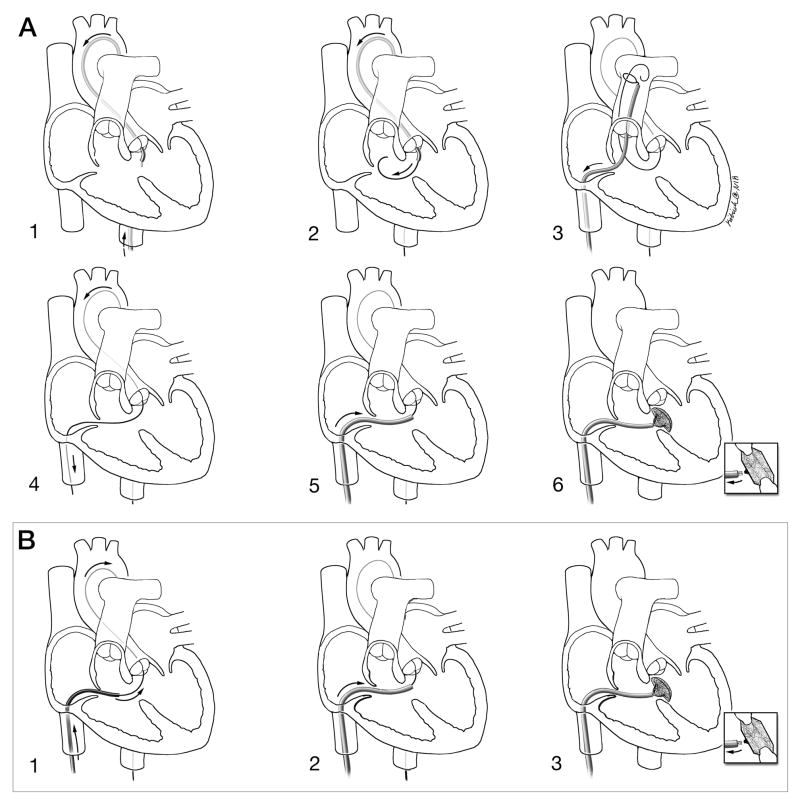
Figure 2. Schematic depictions of conventional and investigational procedure technique.
A: Conventional retrograde X-ray technique. 1: Retrograde, transaortic access to the left ventricle; 2: A guidewire crosses retrograde from the left to right ventricle across the VSD; 3: A transfemoral venous snare retrieves the transaortic guidewire from the pulmonary artery; 4: An arteriovenous loop is exteriorized to provide a rail to deliver the rigid VSD delivery sheath; 5: The delivery sheath is positioned antegrade across the VSD; 6: The VSD occlusion device is positioned and released.
B: Investigational XFM-guided antegrade technique. 1: With enhanced imaging guidance, the guidewire is passed antegrade from the right ventricle through the VSD into the left ventricle and descending aorta; 2: the delivery sheath is positioned in the left ventricle; 3: the VSD occlusion device is positioned and released.
The XFM technique has fewer steps.
Courtesy of Lydia Kibiuk, NIH Medical Arts and Photography Branch.