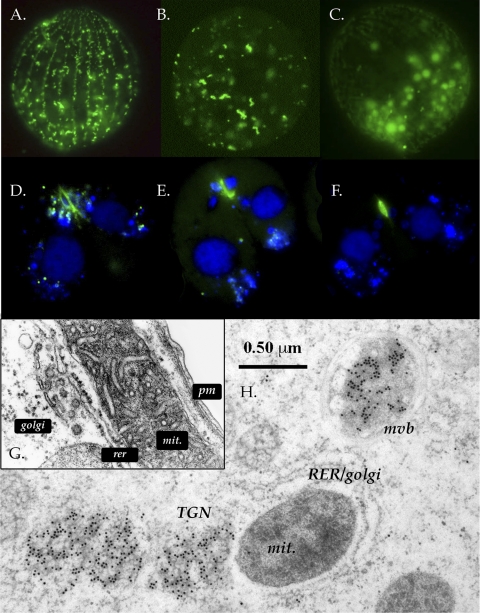
FIG. 5.
Imaging of GFP-tagged Cda13p. Panels A to F are conventional fluorescence micrographs; panels A to C depict vegetative cells, and panels D to F depict conjugating cells. The TEM image in panel H shows vegetative cells. (A) Live-cell fluorescence image of GFP-Cda13p showing a view of the cell cortex. The signal shows up in longitudinal rows of irregularly shaped vesicles docked at the cell cortex. (B) Deep view showing elongated, irregular compartments. (C) Faint autofluorescence of food vacuoles in the background (optical gain was increased to highlight the pattern of autofluorescence). (D) Conjugating cells during nuclear exchange. Nuclei are blue (DAPI stained), and GFP-Cda13p is green. (E and F) Postexchange pairs show residual GFP signals at the nuclear exchange junctions. (G) TEM image showing a wild-type cortex with mitochondrion (mit), plasma membrane (pm), rough endoplasmic reticulum (rer), and Golgi structures. (Copyright Arno Tiedtke.) (H) TEM image of immunogold-labeled GFP-Cda13p-positive material. Gold particles are heavily concentrated over structures resembling multivesicular bodies (mvb) and in a region, positioned away from the rough endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi system, which we hypothesize to be downstream from the trans-Golgi network (TGN).