FIG. 7.
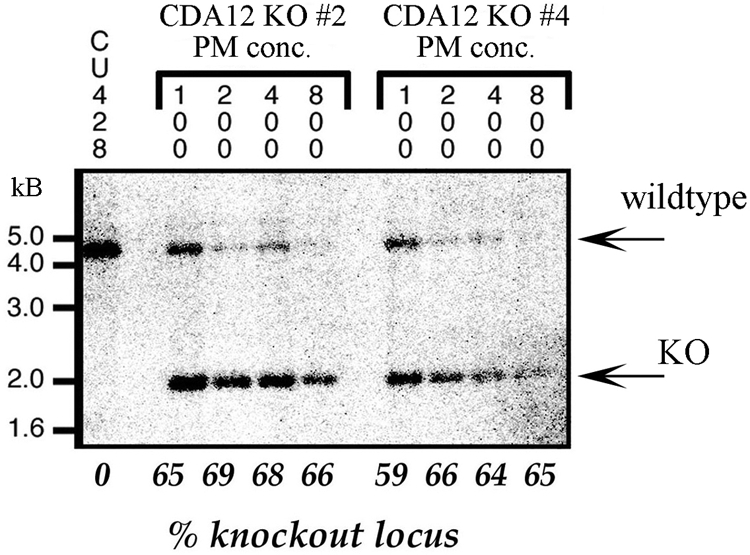
Loss of the wild-type CDA12/CDA13 locus following drug selection for the gene knockout. The CDA12/CDA13 locus was disrupted by the insertion of a selectable neomycin (or paromomycin) resistance gene driven by the histone H4 promoter. Tetrahymena cells were then transformed with this construct, which recombined into the endogenous CDA12/CDA13 locus within the macronucleus. The first lane corresponds to DNA from strain CU428, a wild-type control. Transformant (knockout [KO]) clones 2 and 4 were transferred into media with increasing concentrations (conc.; 100, 200, and 400 μg/ml, etc.) of paromomycin (PM). Numbers across the bottom indicate knockout/wild-type locus ratios from densitometric scans. The wild-type allele runs at 4.2 kb, and the knockout allele runs at 2.3 kb. Despite high drug concentrations (800 μg/ml paromomycin), cells never lost more than 30% of the wild-type CDA12/CDA13 allele.
