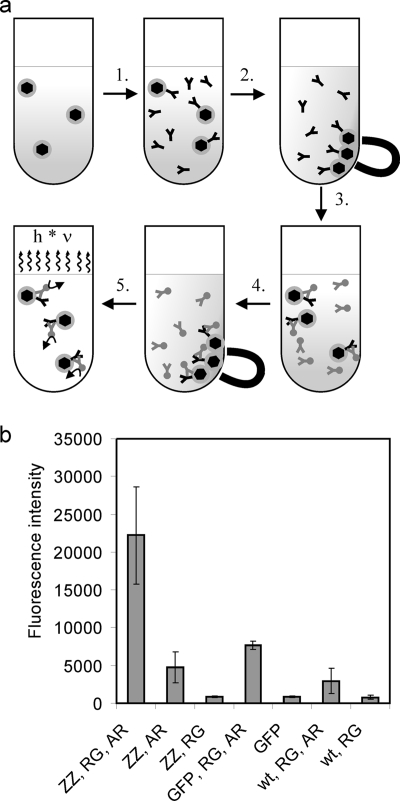
FIG. 3.
Antibody-binding assay of MamC-ZZ magnetosomes. (a) Schematic illustration of the antibody-binding assay procedure. 1. MamC-ZZ modified magnetosomes and controls were diluted to a concentration of 1 mM Fe in 500 μl blocking solution (TBS [20 mM Tris, 0.5 M NaCl, pH 7.5] plus 0.5% [wt/vol] milk powder). The samples were incubated for 30 min at room temperature before rabbit anti-GFP antibody was added at a 1:2,000 dilution. 2. After incubation for 45 min, magnetosomes were magnetically collected and resuspended in TBS. 3. After a second magnetic separation step, a conjugate of shrimp alkaline phosphatase and goat anti-rabbit antibody was added in a 1:2,000 dilution in TBS. 4. After an incubation period of 45 min, the magnetosomes were magnetically separated and washed with TBS three times. 5. The particles were resuspended in 200 μl TBS, of which 100 μl was incubated with 100 μl Attophos shrimp alkaline phosphatase detection reagent (Roche) for 5 min. Fluorescence was detected with an Infinite 500 plate reader (Tecan). The excitation wavelength was 430 nm (20-nm bandwidth), and emission was recorded at 535 nm (25-nm bandwidth). (b) Antibody-binding assay of MamC-ZZ modified magnetosomes. The assay was performed with magnetosomes purified from M. gryphiswaldense pBBRPdcCZZ (ZZ), with MamC-GFP modified magnetosomes (GFP) (from M. gryphiswaldense pCL6 [9]), or with wild-type magnetosomes (wt). The magnetosomes were treated either with a primary rabbit anti-GFP antibody (RG), with a shrimp alkaline phosphatase conjugate of a goat anti-rabbit antibody (AR), or with both antibodies (RG, AR). Standard deviations calculated from three replicates are indicated.